Introduction: Healing Your Body from the Inside Out
Our bodies face daily attacks from free radicals — unstable molecules formed through pollution, stress, processed foods, and even normal metabolism. These radicals damage cells, speed up aging, and contribute to chronic diseases like diabetes, cancer, and heart disease.
That’s where antioxidant therapy comes in. It uses natural or supplemental antioxidants to neutralize free radicals and protect your body’s cells from harm. By balancing oxidative stress, this therapy supports overall health, boosts immunity, and helps in disease prevention.
What Are Antioxidants?
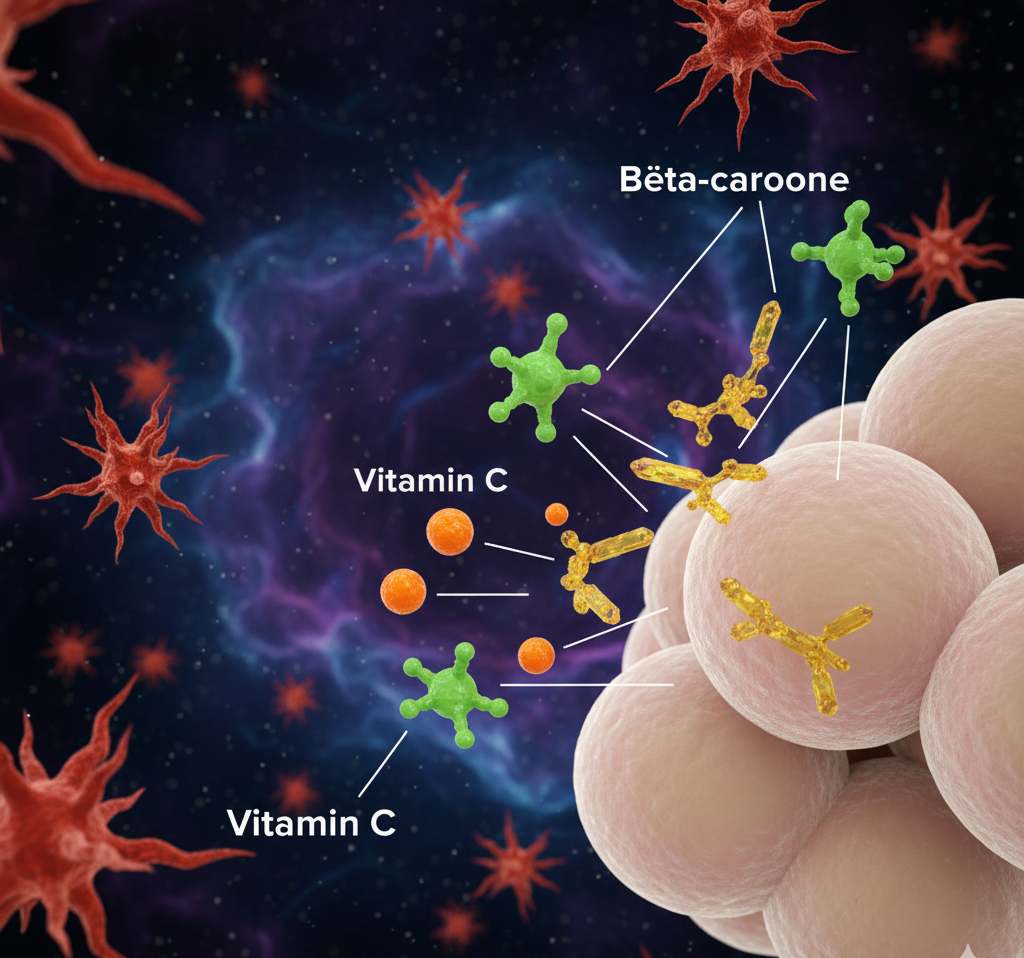
Antioxidants are compounds that prevent or slow damage to cells caused by oxidative stress. They are found naturally in fruits, vegetables, herbs, and certain supplements.
Common antioxidants include:
-
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
-
Vitamin E (tocopherol)
-
Beta-carotene
-
Selenium
-
Zinc
-
Polyphenols (found in green tea, berries, and turmeric)
These compounds act as your body’s “shield,” stabilizing free radicals before they can cause cellular harm.
What Is Antioxidant Therapy?
Antioxidant therapy involves increasing the body’s antioxidant levels — either through diet, supplements, or medical formulations — to counteract oxidative damage.
It’s often used in:
-
Preventive healthcare (to slow aging and maintain vitality)
-
Chronic disease management (diabetes, hypertension, liver disorders)
-
Skin and hair rejuvenation (anti-aging effects)
-
Recovery after illness or surgery
This therapy may include oral supplements, IV infusions, or antioxidant-rich diet plans prescribed by doctors or nutritionists.
How Free Radicals Damage Your Body
Free radicals are unstable molecules that seek stability by stealing electrons from healthy cells. This process leads to oxidative stress, which can damage DNA, proteins, and cell membranes.
Long-term oxidative stress contributes to:
-
Premature aging and wrinkles
-
Heart disease and high blood pressure
-
Cancer development
-
Liver damage
-
Eye disorders (like cataracts)
-
Brain diseases (like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s)
Antioxidant therapy helps neutralize these radicals, reducing cellular damage and inflammation.
Benefits of Antioxidant Therapy
-
Boosts immunity: Strengthens your body’s defense against infections.
-
Delays aging: Reduces fine lines, wrinkles, and cell degeneration.
-
Improves heart health: Lowers cholesterol and prevents plaque formation.
-
Protects liver and kidneys: Detoxifies harmful chemicals.
-
Enhances skin glow: Promotes collagen and cell renewal.
-
Reduces cancer risk: Limits DNA damage caused by free radicals.
-
Supports mental clarity: Protects neurons and boosts brain function.
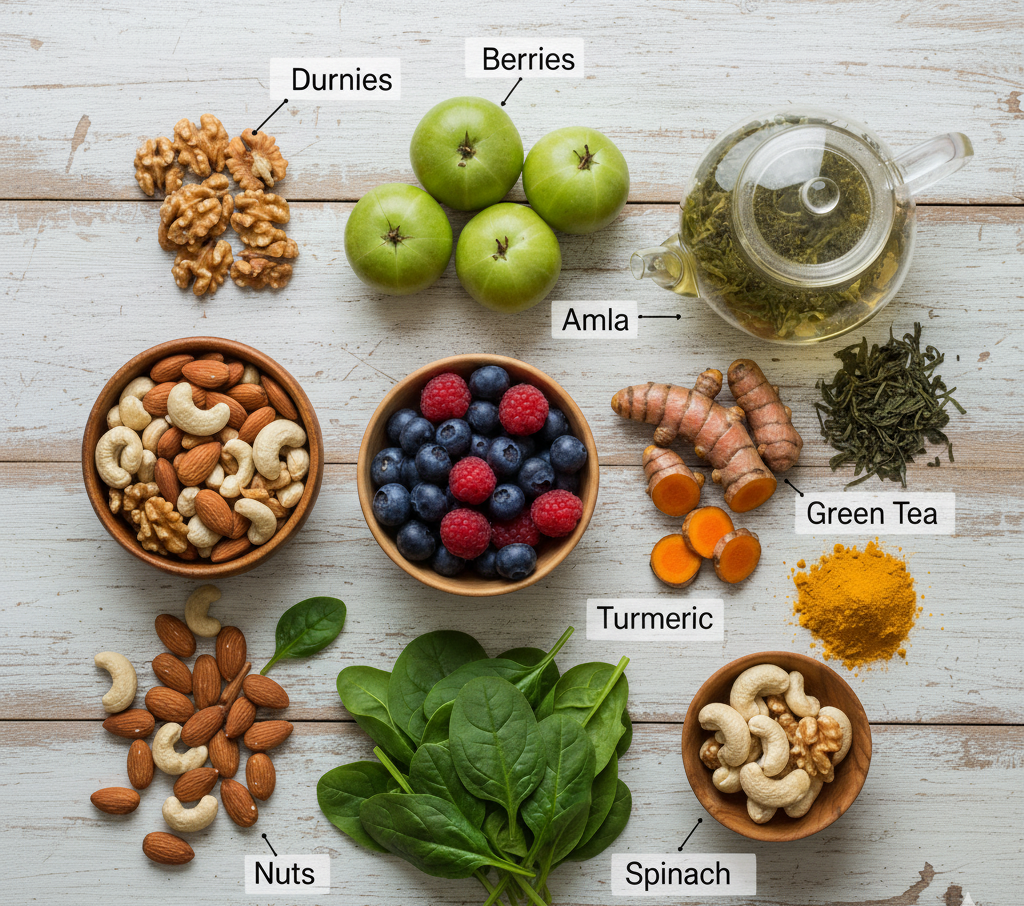

Natural Antioxidants: Power from Plants and Foods
Some of the best sources of natural antioxidants are found right in your kitchen.
Top natural antioxidant foods:
-
Fruits: Amla (Indian gooseberry), oranges, papaya, grapes, berries.
-
Vegetables: Spinach, kale, beetroot, tomatoes, carrots.
-
Herbs & spices: Turmeric (curcumin), tulsi, ginger, garlic.
-
Beverages: Green tea, black coffee (in moderation), herbal infusions.
-
Nuts & seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, sunflower seeds.
-
Dark chocolate: Rich in flavonoids (in small quantities).
These natural antioxidants not only protect your organs but also improve digestion, energy, and skin health.
When Is Antioxidant Therapy Recommended?
Doctors may recommend antioxidant therapy if you have:
-
Chronic fatigue or inflammation
-
Liver disease or exposure to toxins
-
Diabetes or cardiovascular disease
-
Skin dullness or premature aging
-
Nutrient deficiencies
-
Weakened immune system
Types of Antioxidant Therapy
-
Dietary therapy: Emphasizes antioxidant-rich foods.
-
Supplemental therapy: Capsules or tablets containing vitamins and minerals.
-
IV Antioxidant Infusion: Direct delivery of antioxidants into the bloodstream for faster effect.
-
Topical therapy: Creams or serums for skin protection.
Always consult your doctor before starting supplements or IV therapy.
How to Incorporate Antioxidants Daily
-
Start your day with warm lemon water and amla juice.
-
Add turmeric and garlic to meals.
-
Snack on nuts, seeds, and fresh fruits.
-
Drink green tea instead of sugary beverages.
-
Choose colorful vegetables — more colors = more antioxidants.
Precautions and Side Effects
While antioxidants are beneficial, over-supplementation can cause imbalance.
-
Too much vitamin E can thin blood.
-
High doses of beta-carotene may harm smokers.
-
Excessive use of supplements can strain the kidneys or liver.
Tip: Focus on food-based antioxidants unless prescribed supplements.

Prevention Through Antioxidant-Rich Living
-
Eat seasonal fruits and vegetables daily.
-
Avoid smoking and alcohol (they increase oxidative stress).
-
Exercise regularly.
-
Stay hydrated and manage stress.
-
Get enough sleep for natural cell repair.
Conclusion
Antioxidant therapy is a science-backed way to protect your body from inside out. By balancing oxidative stress, it strengthens immunity, slows aging, and reduces chronic disease risk.
The simplest approach? Add more natural antioxidants to your daily diet — fruits, vegetables, herbs, and seeds.
Small lifestyle changes today can protect your cells for years to come.
For expert advice or customized antioxidant plans, consult your doctor via Quickobook for guidance and preventive health check-ups.
Quickobook CTA
Book a consultation with a nutritionist or preventive medicine specialist on Quickobook for antioxidant therapy and diet planning.
Visit Quickobook.com to find verified doctors and easy online appointments.
50 FAQs: Antioxidant Therapy
Q1. What is antioxidant therapy?
It’s a treatment that uses antioxidants to neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative damage.
Q2. What are free radicals?
They are unstable molecules that damage cells, accelerating aging and disease.
Q3. How does antioxidant therapy work?
It increases antioxidant levels in your body through diet or supplements to fight free radicals.
Q4. Is antioxidant therapy safe?
Yes, when supervised by a healthcare professional.
Q5. Can antioxidants prevent aging?
They slow down aging by protecting cells from damage.
Q6. What foods are rich in antioxidants?
Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and green tea.
Q7. Can I take antioxidant supplements daily?
Yes, if prescribed — avoid self-medication.
Q8. Is vitamin C an antioxidant?
Yes, it boosts immunity and neutralizes harmful radicals.
Q9. What’s the best time to take antioxidants?
Morning with meals for better absorption.
Q10. Can antioxidants help with skin health?
Yes, they improve collagen and protect against UV damage.
Q11. Are natural antioxidants better than supplements?
Yes, food-based sources are safer and more balanced.
Q12. Can antioxidant therapy help in liver detox?
Yes, it helps eliminate toxins and supports liver health.
Q13. Does antioxidant therapy prevent cancer?
It may reduce cancer risk by preventing DNA damage.
Q14. Can it boost immunity?
Yes, antioxidants strengthen immune defense.
Q15. Can I overdose on antioxidants?
Yes, high doses of supplements can cause side effects.
Q16. Can antioxidant therapy help diabetes?
It reduces oxidative stress linked to insulin resistance.
Q17. Does cooking destroy antioxidants?
Some nutrients reduce with heat — prefer raw or lightly cooked foods.
Q18. Are antioxidants found in Indian spices?
Yes, turmeric, cloves, cinnamon, and cardamom are powerful antioxidants.
Q19. Can antioxidants help eye health?
Yes, vitamins C and E protect against cataracts and macular degeneration.
Q20. Do antioxidants improve heart health?
Yes, they lower LDL cholesterol and improve blood vessel function.
Q21. Can smoking deplete antioxidants?
Yes, smoking increases free radical damage.
Q22. What are examples of antioxidant supplements?
Vitamin C, vitamin E, selenium, zinc, and coenzyme Q10.
Q23. Can antioxidant therapy reduce stress?
Yes, it helps combat the effects of oxidative stress.
Q24. Can antioxidants brighten skin?
Yes, vitamin C and polyphenols improve skin tone.
Q25. How long does it take to see benefits?
Results appear within weeks to months with consistent use.
Q26. What is oxidative stress?
An imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body.
Q27. Can antioxidants help brain function?
Yes, they protect neurons and may improve memory.
Q28. Are antioxidant drinks helpful?
Only if low in sugar — homemade versions are best.
Q29. Can antioxidant therapy help acne?
Yes, it reduces inflammation and supports skin repair.
Q30. Is green tea a good antioxidant source?
Yes, it’s rich in catechins that reduce oxidative stress.
Q31. Can antioxidants help athletes?
Yes, they reduce muscle fatigue and speed up recovery.
Q32. Can antioxidant therapy help chronic fatigue?
Yes, by reducing cellular damage and boosting energy.
Q33. Do antioxidants improve hair health?
Yes, they strengthen follicles and reduce hair fall.
Q34. Can antioxidants help during recovery from illness?
Yes, they promote faster healing and tissue repair.
Q35. Are antioxidant injections safe?
Yes, under medical supervision (e.g., glutathione therapy).
Q36. Can children take antioxidants?
Only through food — avoid supplements unless prescribed.
Q37. Are antioxidant-rich smoothies effective?
Yes, when made with fresh fruits and no added sugar.
Q38. Can antioxidants protect against pollution?
Yes, they neutralize toxins from smoke and dust exposure.
Q39. Do antioxidants aid weight loss?
They support metabolism but are not a direct fat burner.
Q40. Can antioxidant therapy prevent wrinkles?
Yes, it slows down collagen breakdown.
Q41. Are antioxidants anti-inflammatory?
Yes, they reduce internal inflammation.
Q42. Can antioxidants improve fertility?
Yes, they enhance sperm and egg quality.
Q43. What is the best antioxidant supplement?
Depends on your needs — vitamin C and E are most common.
Q44. Can antioxidant therapy cause allergies?
Rarely — consult your doctor if you have sensitivity.
Q45. Are antioxidant IV drips effective?
Yes, they provide direct absorption for faster results.
Q46. Can I take antioxidants with medicines?
Consult your doctor — some may interact with drugs.
Q47. Is turmeric a natural antioxidant?
Yes, curcumin in turmeric is one of the strongest natural antioxidants.
Q48. How much vitamin C should I take daily?
Usually 65–90 mg/day, but consult your doctor.
Q49. Can antioxidant therapy help post-surgery recovery?
Yes, it aids wound healing and reduces inflammation.
Q50. Where can I consult for antioxidant therapy in India?
Book appointments with specialists via Quickobook.com.









Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!
Leave a Comment