Introduction
Heart attack in India has increased sharply over the last two decades. Earlier, heart attacks were mostly seen in people above 60 years. Today, doctors across India are seeing heart attacks in people as young as 25 to 40 years. This growing trend is worrying for families and healthcare systems alike.
A heart attack, also called myocardial infarction, happens when blood flow to the heart is blocked. This blockage damages the heart muscle and can be life-threatening if not treated quickly. Poor cardiac health, unhealthy lifestyles, stress, and chronic diseases are major contributors to this rise.
This blog explains why heart attacks are increasing in India, common heart attack symptoms, causes, treatment options, and simple steps to protect your heart.

Why Heart Attack in India Is Rising?
India is often called the “heart attack capital of the world.” Studies show Indians develop heart disease nearly 10 years earlier than people in Western countries. Urbanization, lifestyle changes, and lack of preventive care play a major role.
Key reasons include:
-
More sedentary jobs and less physical activity
-
High intake of processed and oily foods
-
Rising stress levels
-
Increase in diabetes and high blood pressure
-
Late diagnosis and poor awareness of heart attack symptoms
According to World Health Organization, cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death in India, accounting for over one-fourth of all deaths.

What Is a Heart Attack?
A heart attack happens when one of the blood vessels supplying the heart gets blocked, usually due to fat deposits called plaque. When plaque breaks, a blood clot forms and stops blood flow.
Without oxygen-rich blood, the heart muscle starts to die. This is why immediate treatment is critical for survival and recovery.
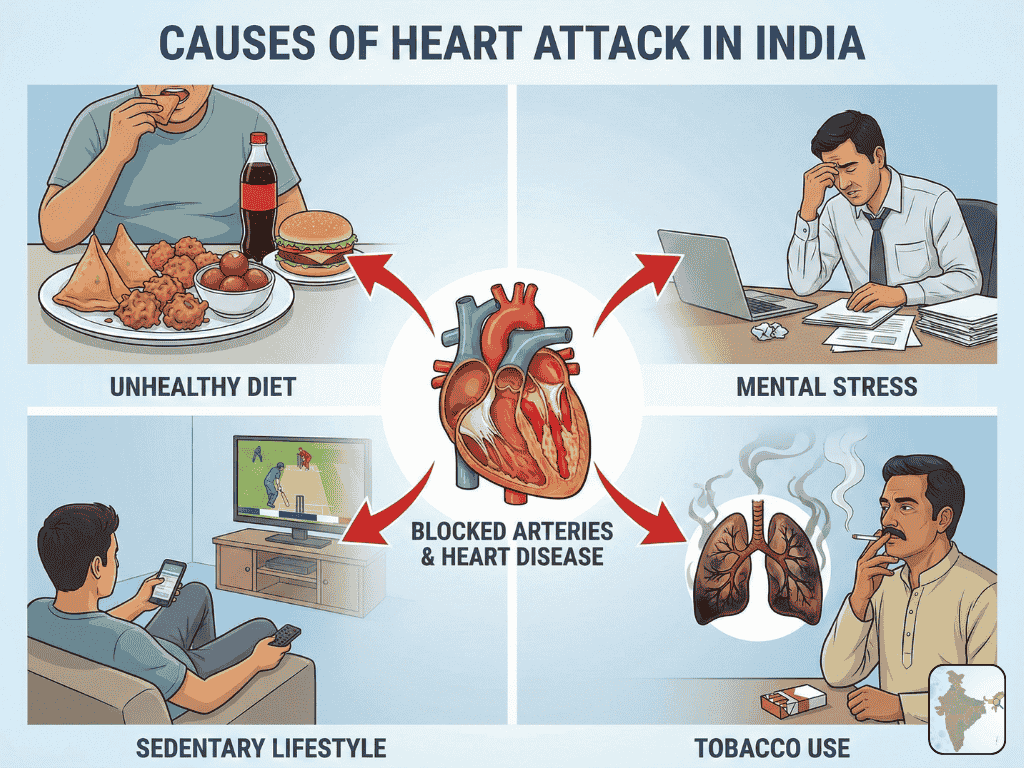
Common Causes of Heart Attack in India
Unhealthy Diet
The typical urban Indian diet is high in salt, sugar, refined flour, and trans fats. Frequent consumption of fried snacks, bakery items, and fast food increases cholesterol levels and damages arteries.
Stress and Heart Attack
Work pressure, financial stress, long working hours, and poor sleep are common in Indian cities. Chronic stress raises blood pressure and heart rate, increasing heart attack risk.
Lack of Physical Activity
Many Indians spend long hours sitting at desks or using mobile phones. Physical inactivity weakens the heart and promotes weight gain.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking damages blood vessels and reduces oxygen in the blood. Smokeless tobacco products like gutkha and pan masala are also harmful to cardiac health.
Diabetes and High Blood Pressure
India has one of the highest numbers of people with diabetes. High blood sugar damages blood vessels, while high blood pressure strains the heart.
Family History
If parents or siblings had a heart attack at an early age, the risk is higher due to genetic factors.
Heart Attack in Young Adults in India
One alarming trend is the rise of heart attacks among young adults. Long working hours, night shifts, lack of exercise, smoking, and poor diet are major reasons.
Young people often ignore early heart attack symptoms, assuming they are “too young” for heart disease. This delay can be dangerous.
Heart Attack Symptoms You Should Never Ignore
Heart attack symptoms may vary from person to person. Common signs include:
-
Chest pain or heaviness, often on the left side
-
Pain spreading to arm, jaw, neck, or back
-
Shortness of breath
-
Cold sweats
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Sudden dizziness or fainting
-
Extreme fatigue
In women, symptoms may be milder and include breathlessness, indigestion-like pain, or unusual tiredness.
Diagnosis of Heart Attack
Doctors use several tests to confirm a heart attack:
-
ECG (electrocardiogram) to check heart rhythm
-
Blood tests to detect heart muscle damage
-
Echocardiogram to assess heart function
-
Angiography to find blocked arteries
Early diagnosis saves lives and reduces complications.
Heart Attack Treatment Options in India
Emergency Treatment
Immediate medicines are given to dissolve clots and reduce heart damage. Oxygen and pain relief may also be provided.
Angioplasty and Stent
Blocked arteries are opened using a balloon and stent. This restores blood flow quickly.
Bypass Surgery
In severe cases, bypass surgery creates a new route for blood flow around blocked arteries.
Medicines
Long-term medicines may include blood thinners, cholesterol-lowering drugs, and blood pressure medicines. Dosage always depends on a doctor’s advice.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Cardiac Health
Small daily habits can make a big difference.
-
Eat more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts
-
Reduce fried, packaged, and sugary foods
-
Exercise at least 30 minutes a day
-
Quit smoking and limit alcohol
-
Practice stress management like yoga or meditation
-
Get 7–8 hours of quality sleep
Prevention: How to Reduce Heart Attack Risk
Prevention is always better than cure.
-
Get regular health checkups
-
Control diabetes, blood pressure, and cholesterol
-
Maintain a healthy weight
-
Manage stress early
-
Learn to recognize heart attack symptoms
Early action can prevent serious complications.
When to See a Doctor Immediately
Seek emergency medical help if you or someone nearby has:
-
Chest pain lasting more than 10 minutes
-
Sudden breathlessness
-
Fainting or collapse
-
Severe sweating with chest discomfort
Do not delay. Every minute matters during a heart attack.
Risks and Complications After a Heart Attack
If not treated properly, a heart attack can lead to:
-
Heart failure
-
Irregular heartbeat
-
Recurrent heart attacks
-
Reduced quality of life
Timely treatment and lifestyle changes reduce these risks.
50 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is a heart attack?
A heart attack happens when blood flow to the heart is blocked, damaging the heart muscle.
Q2. Why is heart attack in India increasing?
Unhealthy lifestyle, stress, diabetes, and poor cardiac health are major reasons.
Q3. Can young people get heart attacks?
Yes, heart attacks are increasingly seen in people below 40 in India.
Q4. What are early heart attack symptoms?
Chest pain, breathlessness, sweating, and nausea are common early signs.
Q5. Is heart attack always sudden?
No, warning signs may appear days or weeks before.
Q6. Can stress cause a heart attack?
Yes, long-term stress increases blood pressure and heart risk.
Q7. Is chest pain always present?
No, some people have mild or unusual symptoms.
Q8. Are women’s symptoms different?
Yes, women may feel fatigue, nausea, or breathlessness instead of chest pain.
Q9. Can diet prevent heart attacks?
Yes, a balanced diet improves cardiac health.
Q10. Is walking good for heart health?
Yes, regular walking strengthens the heart.
Q11. Does smoking increase heart attack risk?
Yes, smoking is a major cause of heart disease.
Q12. Can diabetes lead to heart attack?
Yes, diabetes damages blood vessels.
Q13. What tests diagnose a heart attack?
ECG, blood tests, and angiography are commonly used.
Q14. Is heart attack curable?
Damage cannot be reversed, but further harm can be prevented.
Q15. How long does recovery take?
Recovery varies from weeks to months.
Q16. Can heart attack happen during sleep?
Yes, it can happen anytime.
Q17. Are heart attacks hereditary?
Family history increases risk.
Q18. Can stress tests predict heart attack?
They help assess heart risk.
Q19. Is yoga helpful for cardiac health?
Yes, it reduces stress and improves heart health.
Q20. Can cholesterol cause heart attack?
High cholesterol leads to artery blockage.
Q21. Is alcohol safe for the heart?
Excess alcohol increases heart risk.
Q22. Can heart attacks be silent?
Yes, especially in diabetics.
Q23. What is angioplasty?
A procedure to open blocked heart arteries.
Q24. Are stents permanent?
Yes, stents stay in the artery.
Q25. Can heart attack recur?
Yes, without lifestyle changes.
Q26. Should I stop work after a heart attack?
Only temporarily, as advised by a doctor.
Q27. Can heart attack cause depression?
Yes, emotional changes are common.
Q28. Is bypass surgery risky?
It is generally safe when done on time.
Q29. How often should heart checkups be done?
At least once a year after age 30.
Q30. Is fast food bad for the heart?
Yes, it harms cardiac health.
Q31. Can weight loss reduce heart risk?
Yes, maintaining healthy weight helps.
Q32. Is high BP dangerous for the heart?
Yes, it strains the heart.
Q33. Can heart attack be prevented completely?
Risk can be reduced but not eliminated.
Q34. Is chest burning a heart symptom?
It can be, and should be checked.
Q35. Can anxiety mimic heart attack symptoms?
Yes, but medical evaluation is needed.
Q36. Do heart medicines need lifelong use?
Often yes, as advised by doctors.
Q37. Can lack of sleep cause heart attack?
Yes, poor sleep increases risk.
Q38. Is meditation good for the heart?
Yes, it reduces stress.
Q39. Can heart attack cause sudden death?
Yes, without timely treatment.
Q40. Is pain in left arm serious?
It can be a heart attack sign.
Q41. Can heart attack happen without pain?
Yes, especially in elderly and diabetics.
Q42. Are regular checkups important?
Yes, they detect early heart issues.
Q43. Can exercise trigger heart attack?
Sudden heavy exercise without conditioning can.
Q44. Is Indian food unhealthy for the heart?
Only if oily and processed.
Q45. Can stress tests be painful?
No, they are safe and monitored.
Q46. Is heart disease reversible?
Damage is permanent, but progression can be stopped.
Q47. Can cholesterol be controlled naturally?
Yes, with diet and exercise.
Q48. Is heart attack contagious?
No, it is not infectious.
Q49. Can heart attack be misdiagnosed?
Rarely, but tests confirm it.
Q50. When should I call an ambulance?
Immediately if heart attack symptoms appear.
Conclusion
The increase of heart attack in India is a serious public health concern. Changing lifestyles, rising stress, and poor cardiac health are pushing heart disease to younger ages. The good news is that many heart attacks are preventable with awareness, early diagnosis, and healthy habits.
Protect your heart today by eating well, managing stress, staying active, and never ignoring warning signs.










Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!
Leave a Comment