Introduction
Cancer in Assam has become a serious public health concern. The number of cancer cases is rising every year, and many patients are diagnosed very late. This makes treatment harder and survival lower. Assam, a northeastern state of India, already faces challenges like poverty, rural living, and limited healthcare access. Cancer has added another heavy burden.
This situation is a wake-up call for public health Assam. Strong reforms are needed now. With better awareness, early detection, and stronger health systems, many cancer deaths can be prevented.
This guide explains why cancer is growing in Assam, who is most at risk, and what steps can protect lives.
Overview: Why Cancer Is Rising in Assam
Assam has one of the highest cancer rates in the country. Head and neck cancers are especially common. Oral cancer, throat cancer, and esophageal cancer are seen far more often than in many other states.
Key reasons include high tobacco use, alcohol intake, poor diet, infections, and delayed medical care. Many people live far from cancer hospitals and reach doctors only when symptoms are severe.
Cancer in Assam is not just a medical issue. It reflects deeper problems in education, lifestyle, and public health planning.
Major Causes of Cancer in Assam
Tobacco Use
Tobacco cancer is the biggest cause. People consume tobacco in many forms:
-
Gutkha and khaini
-
Chewing tobacco with betel nut
-
Cigarettes and bidis
Chewing tobacco damages the mouth and throat. This leads to oral cancer, lip cancer, and throat cancer. Tobacco also increases lung cancer risk.
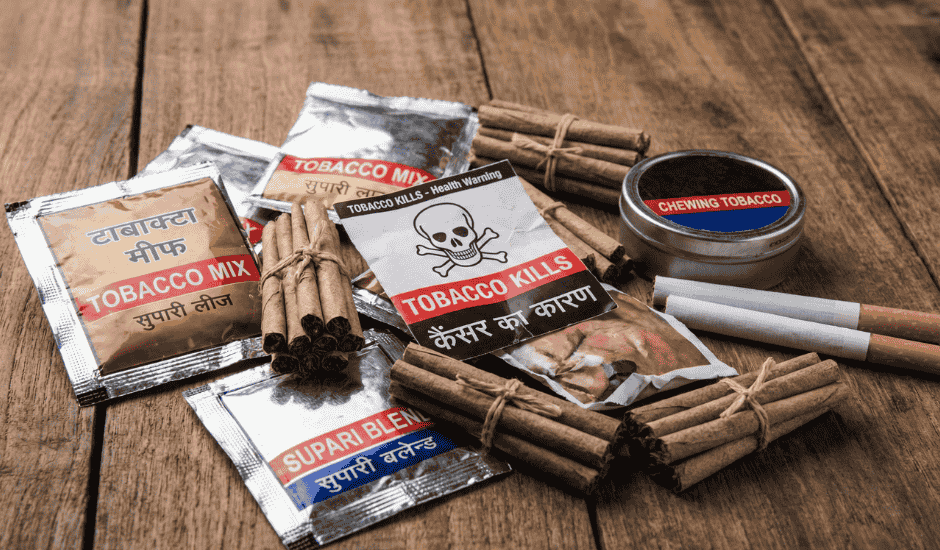

Betel Nut (Areca Nut)
Betel nut chewing is common and socially accepted. It damages mouth tissues and increases cancer risk, especially when mixed with tobacco.
Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol irritates the food pipe and liver. When combined with tobacco, cancer risk becomes much higher.
Poor Diet and Nutrition
Low intake of fruits and vegetables reduces protection against cancer. Many families cannot afford balanced diets.
Infections
Certain infections increase cancer risk:
-
HPV infection can cause oral and cervical cancer
-
Hepatitis B and C can lead to liver cancer
Environmental and Occupational Risks
Pesticide exposure and polluted water sources may also play a role, especially in rural areas.
Common Symptoms People Ignore
Many cancer patients in Assam ignore early signs. Common warning symptoms include:
-
Mouth sores that do not heal
-
White or red patches inside the mouth
-
Difficulty swallowing
-
Long-lasting cough
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Persistent fatigue
-
Lumps in neck or breast
Early symptoms are often painless. This causes dangerous delays.

Diagnosis Challenges in Assam
Late Detection
Most patients are diagnosed at advanced stages. Early screening is rare.
Limited Screening Programs
Regular cancer screening camps are not available in many districts.
Distance from Cancer Centers
Specialist hospitals are mainly in big cities. Travel costs and time delay diagnosis.
Fear and Stigma
Many people fear cancer diagnosis and avoid testing. Myths and shame also prevent early care.
Treatment Options Available
Surgery
Used when cancer is detected early and localized.
Chemotherapy
Medicines that kill cancer cells. Side effects depend on drugs and dose.
Radiation Therapy
High-energy rays used to destroy cancer cells.
Combined Treatment
Many patients need surgery plus chemo or radiation.
Treatment choice depends on cancer type, stage, age, and overall health. Costs can be high, especially for long-term therapy.
Lifestyle Changes That Can Reduce Cancer Risk
Stop Tobacco Use
Quitting tobacco reduces cancer risk at any age.
Reduce Alcohol Intake
Lower alcohol use lowers cancer risk.
Eat a Balanced Diet
More fruits, vegetables, and whole grains protect the body.
Maintain Oral Hygiene
Good mouth care helps reduce oral cancer risk.
Physical Activity
Regular movement improves immunity and health.
Prevention Strategies for Assam
Strong Tobacco Control
Ban on gutkha must be enforced strictly.
Community Awareness
People need simple education in local languages.
School-Based Programs
Teaching children early helps prevent addiction later.
Regular Screening Camps
Oral, breast, and cervical cancer screening should reach villages.
Vaccination
HPV and Hepatitis B vaccines can prevent future cancers.
When to See a Doctor
You should see a doctor immediately if:
-
A mouth ulcer lasts more than two weeks
-
You notice unexplained bleeding
-
Swallowing becomes painful
-
You feel a lump anywhere
-
Weight loss happens without reason
Early care saves lives.
Risks and Complications of Late Treatment
Late-stage cancer leads to:
-
Lower survival chances
-
More aggressive treatment
-
Higher costs
-
Severe pain and disability
-
Emotional stress for families
Early detection reduces suffering and expenses.
Role of Public Health Reform in Assam
Public health Assam needs urgent reform:
-
More cancer centers in districts
-
Mobile screening units
-
Training for local doctors
-
Affordable treatment access
-
Strong anti-tobacco laws
Cancer control must become a priority, not an afterthought.
How Quickobook Can Help
Quickobook helps patients:
-
Book appointments easily
-
Reduce waiting time
-
Access healthcare information
Early consultation through platforms like Quickobook can prevent dangerous delays.
Conclusion
Cancer in Assam is a growing crisis, but it is not hopeless. Many cancers are preventable. Many lives can be saved through early detection. This is a wake-up call for public health reform, stronger awareness, and better access to care.
With the right policies, education, and community action, Assam can fight cancer more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Why is cancer common in Assam?
A. High tobacco use, betel nut chewing, and late diagnosis are major reasons.
Q2. Which cancer is most common in Assam?
A. Oral and head-neck cancers are most common.
Q3. Is chewing tobacco more harmful than smoking?
A. Yes, chewing tobacco greatly increases oral cancer risk.
Q4. Can oral cancer be cured?
A. Yes, if detected early.
Q5. What are early signs of oral cancer?
A. Mouth ulcers, white patches, and pain.
Q6. Does betel nut alone cause cancer?
A. Yes, long-term use increases risk.
Q7. Are women at risk too?
A. Yes, especially for breast and cervical cancer.
Q8. Can cancer be prevented?
A. Many cancers can be prevented with lifestyle changes.
Q9. Is cancer treatment expensive?
A. It can be costly, especially at late stages.
Q10. Does quitting tobacco help after years of use?
A. Yes, risk reduces over time.
Q11. Are cancer screenings painful?
A. Most are simple and painless.
Q12. What age should screening start?
A. It depends on cancer type and risk factors.
Q13. Is cancer contagious?
A. No, cancer does not spread person to person.
Q14. Can poor diet cause cancer?
A. Poor nutrition increases risk.
Q15. Does alcohol alone cause cancer?
A. It increases risk, especially with tobacco.
Q16. Are rural people more affected?
A. Yes, due to limited healthcare access.
Q17. Can HPV cause cancer?
A. Yes, HPV can cause oral and cervical cancer.
Q18. Is vaccination helpful?
A. Yes, vaccines prevent certain cancers.
Q19. Do all cancers cause pain?
A. No, early cancer may not hurt.
Q20. Why do people delay treatment?
A. Fear, cost, and lack of awareness.
Q21. Can cancer come back after treatment?
A. Sometimes, regular follow-up is needed.
Q22. Is traditional medicine enough?
A. No, medical treatment is essential.
Q23. Can stress cause cancer?
A. Stress alone does not cause cancer.
Q24. Are children affected by cancer?
A. Yes, but it is less common.
Q25. Does family history matter?
A. Yes, genetics can increase risk.
Q26. Can pollution cause cancer?
A. Long-term exposure may increase risk.
Q27. Is cancer always fatal?
A. No, many people survive cancer.
Q28. Can early cancer be cured fully?
A. Yes, many early cancers are curable.
Q29. Are free cancer services available?
A. Some government schemes provide support.
Q30. Should mouth sores be checked?
A. Yes, if they last more than two weeks.
Q31. Can diet improve recovery?
A. Yes, good nutrition supports healing.
Q32. Are men more affected than women?
A. Certain cancers are more common in men.
Q33. Does smoking bidis cause cancer?
A. Yes, bidis are harmful.
Q34. Is weight loss a cancer sign?
A. Unexplained weight loss can be a warning sign.
Q35. Can exercise prevent cancer?
A. It reduces risk and improves health.
Q36. Is cancer treatment painful?
A. Side effects vary, doctors manage pain.
Q37. Can early tests save money?
A. Yes, early treatment costs less.
Q38. Are screenings safe?
A. Yes, they are safe and recommended.
Q39. Can cancer affect mental health?
A. Yes, emotional support is important.
Q40. Should family members get tested?
A. If advised by a doctor, yes.
Q41. Is oral hygiene important?
A. Yes, it helps reduce oral cancer risk.
Q42. Can infections lead to cancer?
A. Some infections increase risk.
Q43. Is cancer common only in adults?
A. Mostly, but children can be affected.
Q44. Does late treatment reduce survival?
A. Yes, early treatment improves survival.
Q45. Can mobile screening help rural areas?
A. Yes, it improves early detection.
Q46. Are myths harmful?
A. Yes, they delay care.
Q47. Can awareness reduce cancer cases?
A. Yes, awareness saves lives.
Q48. Should tobacco bans be stricter?
A. Yes, enforcement is essential.
Q49. Can technology help healthcare access?
A. Yes, platforms like Quickobook help.
Q50. Is cancer in Assam preventable?
A. Many cases are preventable with action.








Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!
Leave a Comment