Introduction
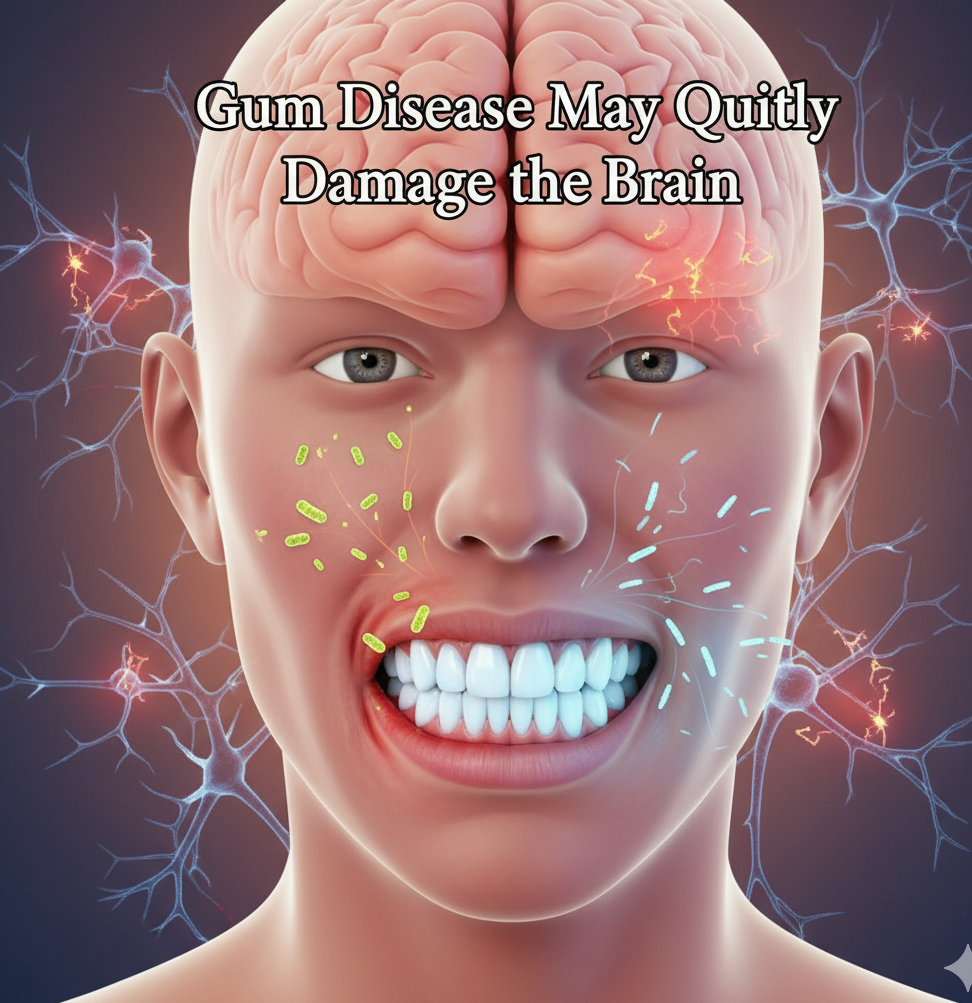
Your mouth might reveal more about your brain than you think. Recent scientific studies show that gum disease, often considered just a dental issue, could actually affect brain health. Researchers have discovered that bacteria and inflammation from the mouth may travel to the brain, increasing the risk of memory loss, Alzheimer’s disease, and other forms of cognitive decline.
In India, where oral hygiene is often overlooked, millions live with untreated gum problems that might silently impact not only their teeth but also their mental sharpness. Let’s explore how this connection works — and what you can do to safeguard both your smile and your brain.
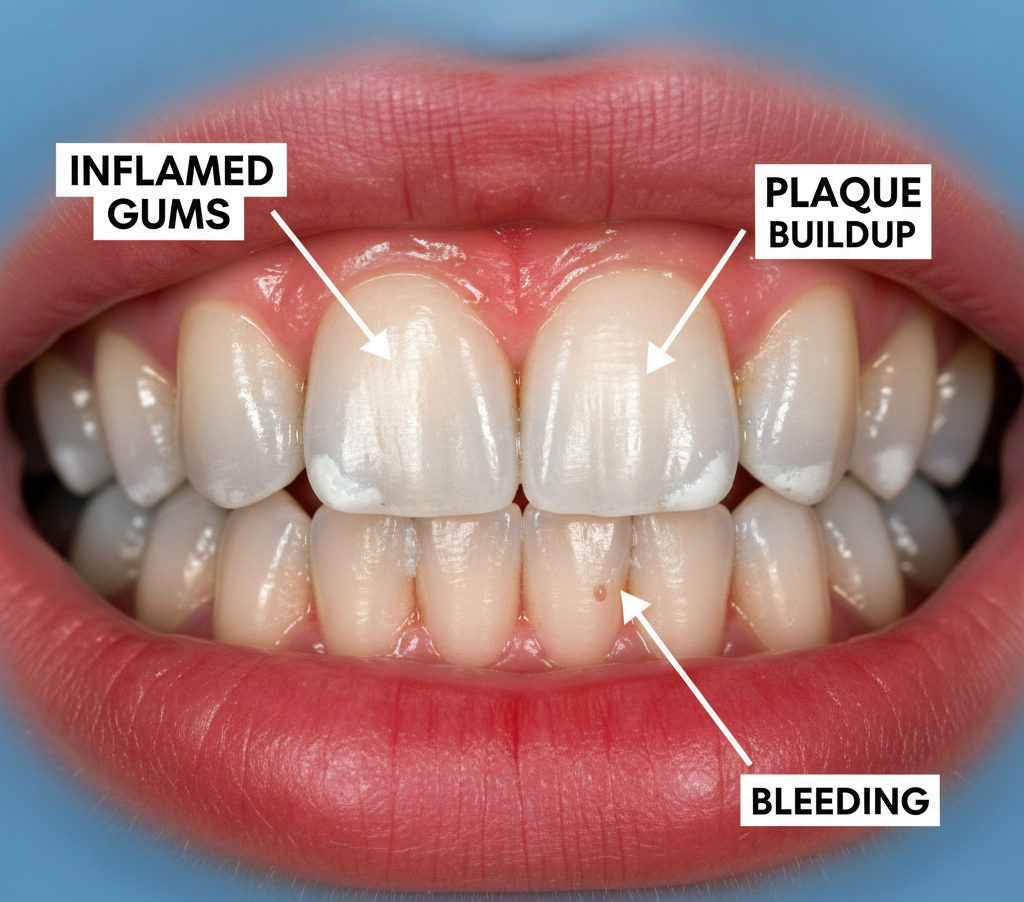
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, medically called periodontitis, is an infection and inflammation of the gums that support your teeth. It usually starts as gingivitis — swollen, red, or bleeding gums — and, if untreated, can damage the bone and tissues holding the teeth in place.
Common symptoms:
- Bleeding gums while brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums
- Loose teeth
- Pus between teeth and gums
If not treated, gum disease can become chronic, leading to tooth loss and systemic inflammation — which is where the brain connection begins.
How Gum Disease Affects the Brain
Researchers have found that bacteria from infected gums can enter the bloodstream and reach the brain, triggering inflammation. The most studied bacterium, Porphyromonas gingivalis, has been detected in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s disease.
ALSO READ: Why Pomegranate Is Good For You: Evidence-based Insights Into Its Health Benefits
The biological chain:
- Gum infection →
- Bacterial toxins enter the bloodstream →
- Brain inflammation →
- Neuronal (nerve cell) damage →
- Memory loss and cognitive decline
Chronic inflammation caused by gum disease can also disrupt blood flow to the brain, worsening brain health and increasing the risk of stroke.
The Science Behind the Mouth–Brain Connection
- Inflammation Link: Gum disease triggers a systemic inflammatory response. Over time, this can damage blood vessels in the brain.
- Toxin Production: Oral bacteria release enzymes called gingipains, which can destroy brain neurons.
- Immune System Overload: Constant infection forces the immune system to overreact, harming healthy brain cells.
- Plaque in Brain and Teeth: Just like plaque forms on teeth, similar protein plaques (amyloid-beta) form in Alzheimer’s patients’ brains — both influenced by bacterial activity.
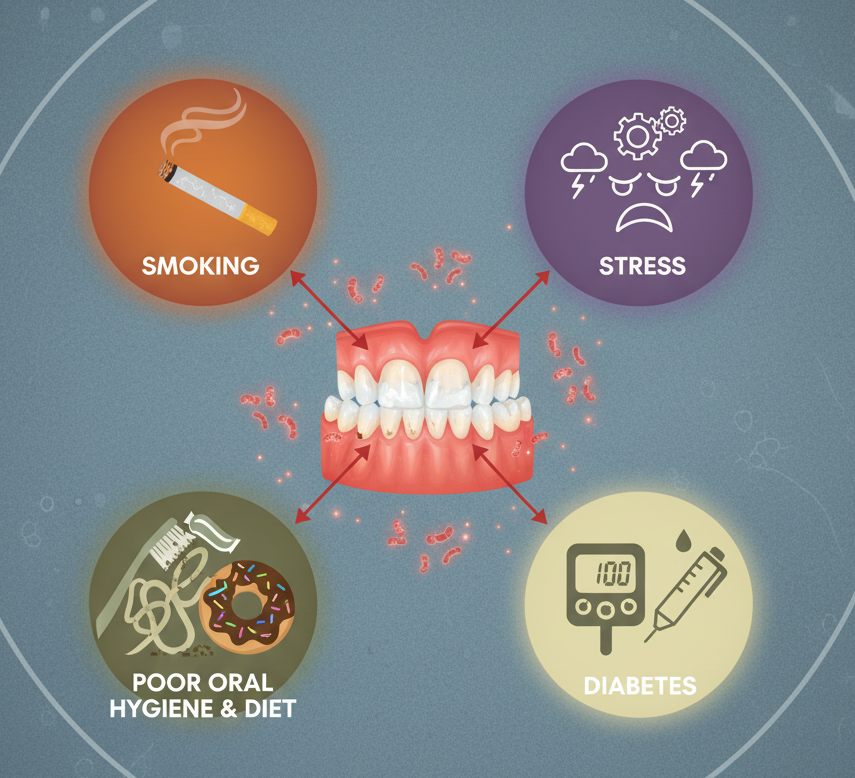
Causes and Risk Factors
You’re more likely to develop gum disease if you have:
- Poor oral hygiene habits (irregular brushing/flossing)
- Smoking or tobacco chewing
- Diabetes
- Stress or hormonal changes
- Family history of dental disease
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Aging
In India, tobacco chewing and poor dental visits are leading causes of gum problems, especially in rural and semi-urban areas.
Early Symptoms to Watch
If you notice any of the following, schedule a dental check-up immediately:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bad breath that doesn’t go away
- Loose teeth or changing bite pattern
- Gums pulling away from teeth
- Bleeding while brushing
Early diagnosis and treatment can reverse gingivitis and prevent irreversible periodontitis.
Diagnosis and Testing
Your dentist may:
- Examine your gums for bleeding, swelling, or pockets.
- Use a periodontal probe to measure gum depth.
- Recommend dental X-rays to check bone loss.
- Suggest blood sugar and vitamin D tests (as they affect gum health).
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on severity:
1. Professional Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing):
Removes plaque and tartar buildup below the gum line.
2. Antibiotic Therapy:
Topical or oral antibiotics to eliminate infection.
3. Laser Treatment:
Minimally invasive removal of diseased tissue and bacteria.
4. Surgical Procedures:
Flap surgery or bone grafting in advanced cases.
5. Lifestyle Modifications:
Quit smoking, maintain oral hygiene, eat balanced meals rich in Vitamin C and calcium.
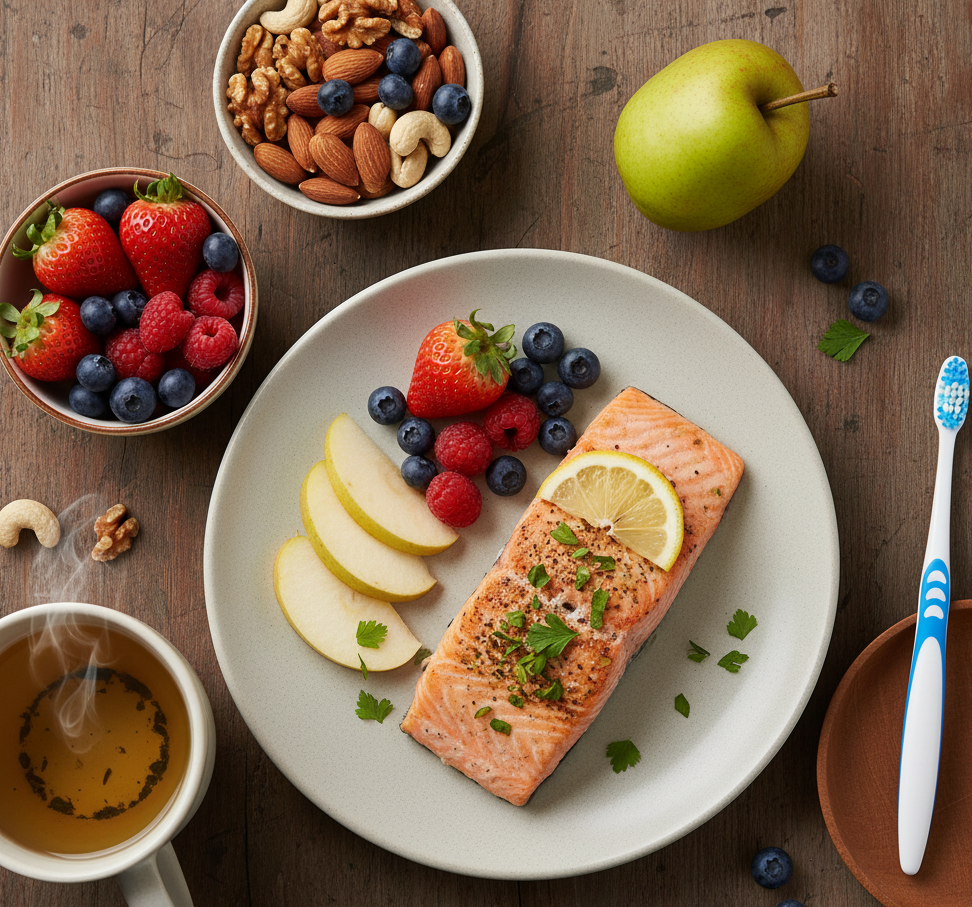
Diet and Lifestyle Tips for Healthy Gums and Brain
- Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss once a day to remove hidden debris.
- Eat omega-3-rich foods (fish, walnuts, flaxseeds) to reduce inflammation.
- Include antioxidants (fruits, vegetables, green tea).
- Stay hydrated — dry mouth increases bacterial growth.
- Exercise regularly — improves blood circulation to gums and brain.

Prevention Is Better Than Treatment
- Schedule dental check-ups every 6 months.
- Avoid tobacco in any form.
- Manage diabetes and blood pressure.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash.
- Replace your toothbrush every 3 months.
These simple steps can save not only your teeth but potentially your brain function too.
When to See a Doctor
See a dentist or periodontist if you notice persistent gum bleeding, bad breath, or loose teeth.
Consult a neurologist if you experience memory lapses, confusion, or unusual fatigue, especially with a history of gum disease.
Risks and Complications
Untreated gum disease can lead to:
- Tooth loss
- Chronic inflammation
- Heart disease and diabetes worsening
- Alzheimer’s and memory loss
- Stroke
Protecting Brain Health Through Oral Care
Remember — your mouth is the gateway to your body. Keeping it clean helps your immune system, heart, and brain function optimally. Regular dental visits, along with a healthy lifestyle, can help prevent diseases that quietly erode mental clarity over time.

Conclusion
Gum disease isn’t just a dental issue — it’s a whole-body concern. Emerging science shows that maintaining oral hygiene can protect your brain from inflammation and degeneration. Don’t wait until symptoms worsen; act early to protect both your smile and your memory.
Book Your Dental Visit with Quickobook
Quickobook connects you with trusted dentists and general physicians across India for easy, affordable appointments.
Book a dental or oral health check-up today at Quickobook.com and keep your gums and brain healthy for life.
50 Frequently Asked Questions on Gum Disease and Brain Health
Q1. What is gum disease?
A. Gum disease is an infection of the gums that causes swelling, bleeding, and damage to the tissues supporting the teeth.
Q2. How can gum disease affect the brain?
A. Bacteria from infected gums can enter the bloodstream, travel to the brain, and cause inflammation linked to memory loss and Alzheimer’s.
Q3. What are the early signs of gum disease?
A. Bleeding while brushing, red or swollen gums, bad breath, and loose teeth are early warning signs.
Q4. Can gum disease really cause brain damage?
A. Studies suggest that chronic gum infections may contribute to brain inflammation and cognitive decline over time.
Q5. Which bacteria are linked to brain problems from gum disease?
A. Porphyromonas gingivalis is the main bacterium found in both infected gums and Alzheimer’s-affected brains.
Q6. How common is gum disease in India?
A. More than 50% of Indian adults have some form of gum disease, often due to poor oral hygiene and tobacco use.
Q7. Can gum disease cause memory loss?
A. Yes, ongoing inflammation from gum disease may affect memory and increase the risk of dementia.
Q8. How does inflammation connect the mouth and brain?
A. Inflammation from gum infection releases chemicals that damage blood vessels and nerve cells in the brain.
Q9. Can brushing prevent brain-related issues?
A. Regular brushing and flossing lower gum inflammation and may reduce risks of brain decline.
Q10. Is Alzheimer’s linked to oral bacteria?
A. Research has found oral bacteria and toxins in Alzheimer’s patients’ brains, suggesting a connection.
Q11. Who is at higher risk of gum disease?
A. Smokers, diabetics, and those with poor oral hygiene or low immunity face higher risk.
Q12. Can gum disease lead to stroke?
A. Yes, chronic inflammation from gum infections can increase stroke risk by affecting blood vessels.
Q13. How can I test for gum disease?
A. A dentist can check for bleeding gums, pocket depth, and bone loss through X-rays.
Q14. Can mouthwash help prevent brain inflammation?
A. Antibacterial mouthwash helps reduce gum bacteria, lowering the spread of toxins that may harm the brain.
Q15. How often should I visit the dentist?
A. At least twice a year for cleaning and early detection of gum issues.
Q16. Does bad breath mean gum disease?
A. Persistent bad breath is often an early symptom of gum infection.
Q17. What foods help strengthen gums?
A. Vitamin C–rich foods like oranges, amla, and spinach strengthen gum tissue and immunity.
Q18. Can stress cause gum disease?
A. Yes, stress weakens immunity, making gums more prone to infection.
Q19. What is periodontitis?
A. It’s an advanced form of gum disease where the bone supporting the teeth begins to deteriorate.
Q20. Can children get gum disease?
A. Yes, poor brushing habits and sugary foods can cause gum problems even in children.
Q21. Is gum bleeding normal during brushing?
A. No, bleeding is a sign of inflammation and should be checked by a dentist.
Q22. Can gum disease be reversed?
A. Gingivitis can be reversed with proper care, but periodontitis requires professional treatment.
Q23. What is scaling and root planing?
A. A dental procedure that cleans plaque and tartar from under the gumline to prevent infection.
Q24. Are antibiotics used for gum disease?
A. Yes, dentists may prescribe antibiotics to control infection and inflammation.
Q25. Can poor dental care increase dementia risk?
A. Evidence suggests poor oral hygiene and gum infections may increase the risk of dementia.
Q26. How can diabetics protect their gums?
A. Maintain good sugar control, brush twice daily, and schedule regular dental visits.
Q27. Can mouth bacteria enter the bloodstream?
A. Yes, through bleeding gums or dental infections, bacteria can reach other body organs.
Q28. What role does plaque play in gum disease?
A. Plaque is a sticky bacterial film that triggers gum inflammation and infection.
Q29. Does tobacco worsen gum disease?
A. Yes, smoking and chewing tobacco damage gums and reduce blood flow needed for healing.
Q30. Can gum disease affect heart health too?
A. Yes, inflammation from the gums can strain the heart and increase the risk of heart disease.
Q31. Are brain and gum diseases connected through inflammation?
A. Yes, both share inflammation as a root cause of tissue damage.
Q32. What are gingipains?
A. Gingipains are toxic enzymes produced by oral bacteria that can harm brain cells.
Q33. Can probiotics help gum and brain health?
A. Yes, probiotics support good oral bacteria and reduce inflammation throughout the body.
Q34. How long does gum treatment take?
A. Mild cases may improve within weeks, while advanced periodontitis may need several sessions.
Q35. Can home remedies cure gum disease?
A. Home care helps mild cases, but professional cleaning is needed for severe infection.
Q36. What is the link between gum disease and aging?
A. Aging weakens immunity and oral tissues, making gums more vulnerable to infection.
Q37. Does tooth loss affect brain function?
A. Yes, tooth loss reduces chewing activity, which is linked to lower brain stimulation.
Q38. Can brushing alone prevent gum disease?
A. Brushing helps, but flossing and professional cleaning are equally important.
Q39. What is the best toothbrush for gum health?
A. A soft-bristled toothbrush minimizes gum irritation and cleans effectively.
Q40. Can poor oral hygiene affect mental health?
A. Yes, dental pain and infection can cause stress, anxiety, and reduced self-esteem.
Q41. Is gum disease painful?
A. Early stages may be painless, which is why regular check-ups are important.
Q42. Can Alzheimer’s patients have worse oral health?
A. Yes, memory issues often lead to neglect of oral hygiene in Alzheimer’s patients.
Q43. How can caregivers help older adults maintain oral health?
A. Assist with brushing, ensure dental visits, and encourage soft, nutritious foods.
Q44. Does genetic history affect gum disease risk?
A. Yes, some people are genetically more prone to gum inflammation.
Q45. Can dry mouth cause gum problems?
A. Yes, saliva protects against bacteria, and reduced flow increases gum infection risk.
Q46. What vitamins help prevent gum disease?
A. Vitamin C, D, and calcium strengthen gum tissues and support healing.
Q47. Can I prevent gum disease naturally?
A. Yes, with consistent brushing, flossing, and eating antioxidant-rich foods.
Q48. Are mouth ulcers related to gum disease?
A. Not directly, but both can occur due to poor oral hygiene or infection.
Q49. When should I see a dentist for bleeding gums?
A. If bleeding persists for more than three days, visit a dentist immediately.
Q50. How can Quickobook help with gum disease care?
A. Quickobook connects you with verified dentists across India for easy appointments, online consultations, and affordable dental care.









Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!
Leave a Comment