Introduction
For decades, conversations around fertility have focused mostly on women. However, new research reveals that male fertility also declines with age, and the impact runs deeper than once thought. Studies now show that as men grow older, their sperm undergo hidden genetic and molecular changes, making conception more difficult and sometimes risky for future children.
In this article, we’ll uncover how male fertility changes with age, why sperm quality declines after 40, and how aging increases sperm DNA fragmentation—all backed by science. Plus, we’ll share how to test sperm quality at home and ways to maintain reproductive health naturally.
Understanding Male Fertility and Aging
Male fertility refers to a man’s ability to impregnate a partner through healthy sperm count, motility (movement), and DNA integrity. While men don’t experience menopause like women, aging still impacts sperm production and health.
| Age Group | Sperm Changes Observed | Fertility Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 20–30 years | Peak sperm count, strong motility | High fertility potential |
| 30–40 years | Mild decline in motility, increased DNA errors | Slightly lower conception rate |
| 40–50 years | Noticeable sperm DNA fragmentation | Reduced fertility, higher genetic risk |
| 50+ years | Lower sperm volume and morphology changes | Increased risk of miscarriage or disorders |
As men age, oxidative stress, hormonal changes, and DNA mutations accumulate, reducing the quality and safety of sperm.
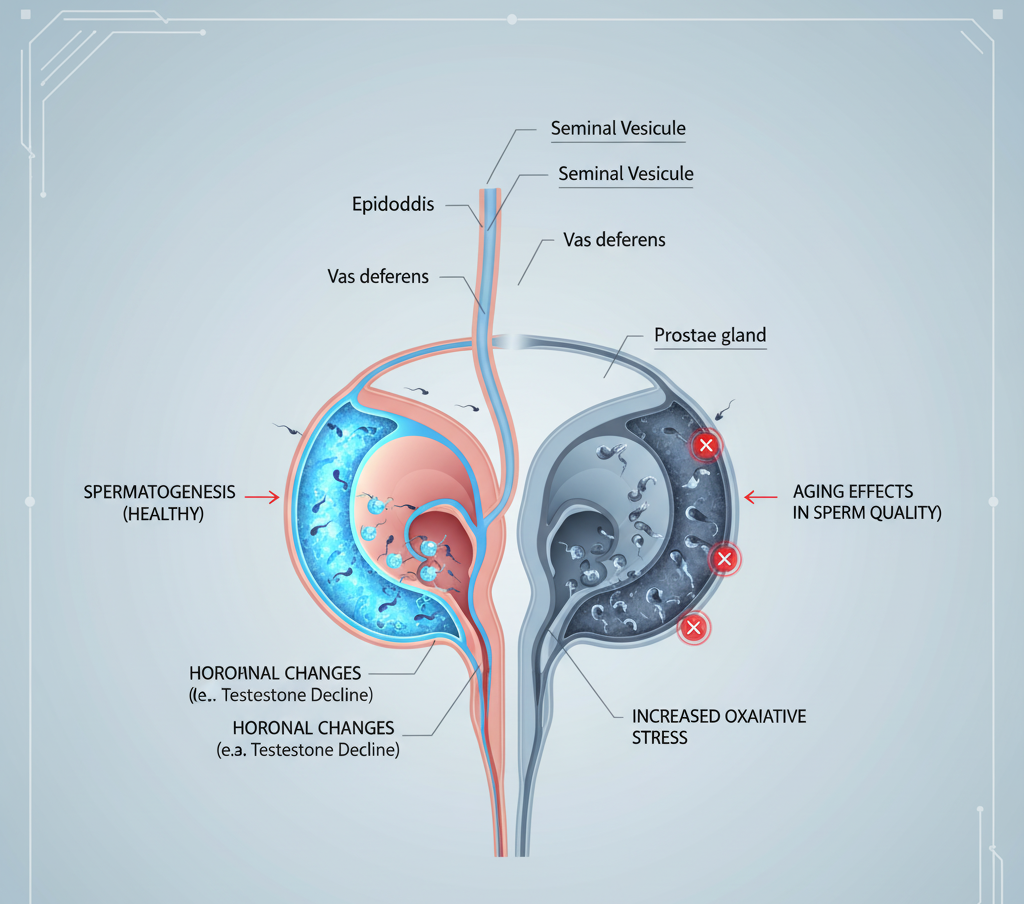
How Male Fertility Changes with Age
Sperm production never truly stops, but the process becomes less efficient. The germline cells in the testes—responsible for producing sperm—divide millions of times over a man’s lifetime. Each division increases the chance of genetic errors.
Key Biological Changes:
-
DNA Mutations: Each sperm carries a slightly different DNA code. As men age, random mutations increase, some linked to autism, schizophrenia, and rare genetic diseases.
-
Hormonal Decline: Testosterone levels drop 1% each year after 30, affecting sperm volume and libido.
-
Oxidative Stress: Exposure to pollution, smoking, alcohol, and unhealthy diets leads to free radicals that damage sperm DNA.
-
Epigenetic Changes: Certain genes switch “on” or “off,” altering sperm’s ability to support healthy embryo development.
These microscopic changes make older sperm biologically “riskier,” even if the man appears healthy.
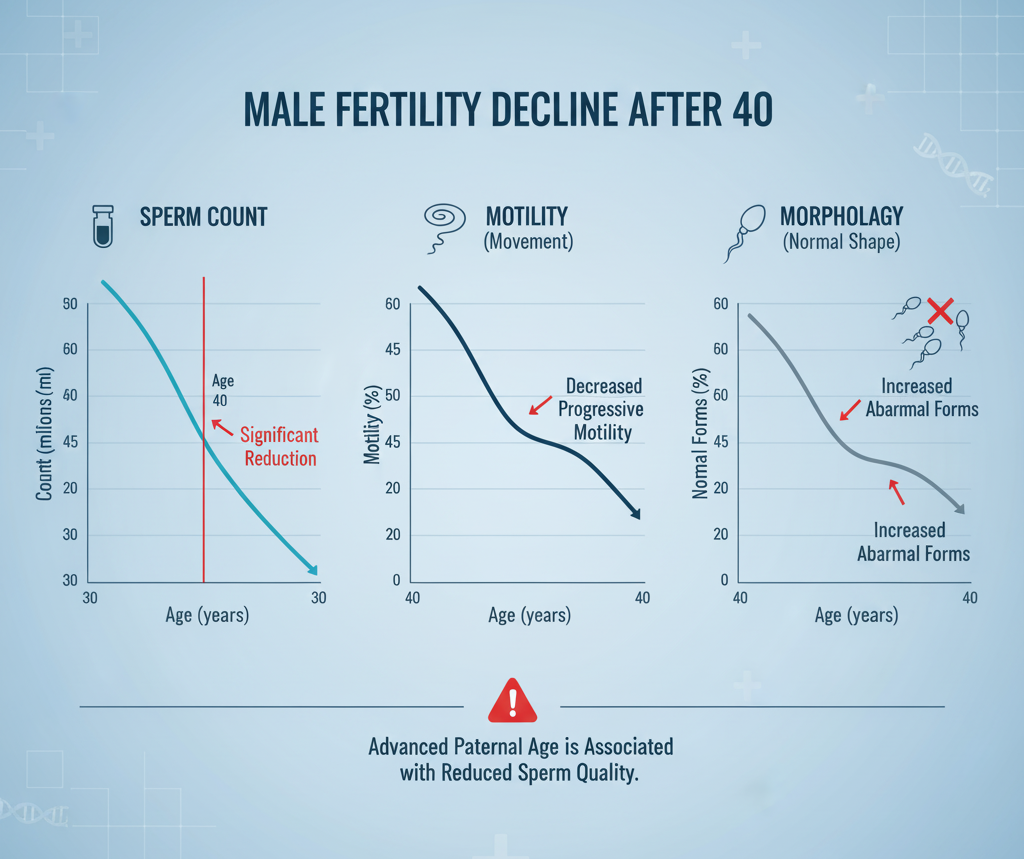
Does Sperm Quality Decline After 40?
Yes — studies confirm that sperm quality begins to drop significantly after age 40.
| Sperm Parameter | Effect of Age (40+) |
|---|---|
| Sperm Count | Decreases by 30–40% |
| Motility | Reduced by 20–25% |
| Morphology | More abnormal shapes observed |
| DNA Integrity | Fragmentation increases by up to 2x |
| Fertility Rate | Pregnancy chances drop by 25–35% |
Older sperm are more likely to carry fragmented DNA, which affects embryo development and increases miscarriage risk.
Quick Fact: A 2023 study found that men over 45 were twice as likely to father children with rare genetic mutations compared to those under 30.
Impact of Aging on Sperm DNA Fragmentation
Sperm DNA fragmentation refers to breaks or damage in the genetic material within sperm cells. It’s one of the key indicators of male fertility decline.
| Cause | Impact on Sperm DNA |
|---|---|
| Oxidative stress | Causes DNA strand breaks |
| Inflammation | Disrupts sperm membrane stability |
| Heat exposure | Impairs DNA repair mechanisms |
| Aging | Increases mutation accumulation |
When sperm DNA fragmentation is high:
-
Fertilization rates drop.
-
Embryos fail to implant.
-
Miscarriage risk increases.
-
Children face higher genetic risk of developmental disorders.
How to Detect It
The Sperm DNA Fragmentation Test (DFI Test) can measure the level of DNA damage. Many Indian fertility centers and labs offer this test. A score below 15% indicates healthy DNA, while over 30% suggests severe damage.
How to Test Sperm Quality at Home
Technology now allows men to monitor fertility conveniently from home.
| Test Type | Measures | Available Brands in India |
|---|---|---|
| At-home sperm test kit | Sperm count and motility | ExSeed, YO Sperm Test, Fertility Tracking Apps |
| Lab-based semen analysis | Count, motility, morphology | Apollo Diagnostics, Lal Path Labs |
| DNA fragmentation test | Sperm DNA integrity | Nova IVF, Indira IVF, Cloudnine Fertility |
These tests provide insights but cannot replace a full medical evaluation. If results show poor sperm health, it’s best to consult a fertility specialist or urologist.
Fatherhood Risks with Age
The fatherhood risks associated with older age go beyond fertility alone. As sperm accumulate DNA damage, there’s an increased chance of genetic anomalies in offspring.
| Condition | Possible Link to Paternal Age |
|---|---|
| Autism Spectrum Disorders | Higher risk in children of fathers >45 years |
| Schizophrenia | Associated with older paternal sperm mutations |
| Down Syndrome | Increased chromosomal abnormalities |
| Miscarriages | Due to poor sperm DNA integrity |
Despite these risks, many older men successfully become fathers. The key lies in maintaining healthy lifestyle habits and early fertility screening.
Improving Sperm Quality Naturally
Even though aging is inevitable, certain lifestyle changes can slow sperm damage and improve male fertility.
| Habit | Fertility Benefit |
|---|---|
| Quit smoking and alcohol | Reduces oxidative DNA damage |
| Exercise regularly | Boosts testosterone and blood flow |
| Eat antioxidant-rich foods | Berries, nuts, spinach improve sperm motility |
| Stay hydrated | Supports semen volume |
| Avoid heat exposure | Keep laptops off laps and avoid tight clothing |
| Manage stress | Lowers cortisol, stabilizes hormones |
When to See a Doctor
You should consult a urologist or fertility specialist if you:
-
Have been trying to conceive for over 6 months without success.
-
Are over 40 and planning for fatherhood.
-
Notice changes in libido or erectile function.
-
Have a history of testicular injury, infection, or surgery.
Early testing and guidance can help detect issues before they become barriers to conception.
Conclusion
The hidden evolution of sperm with age reveals that men’s fertility health deserves as much attention as women’s. Aging doesn’t mean the end of fatherhood—but it does mean being proactive about reproductive health. Through balanced nutrition, avoiding toxins, and regular screening, men can safeguard not just fertility, but also their children’s genetic future.
Quickobook CTA
Concerned about your fertility or planning fatherhood after 40? Book an appointment with an andrologist or fertility specialist on Quickobook today to get expert testing and personalized guidance.
FAQs (50 Expert Answers)
1. Does male fertility decline with age?
Yes, sperm quality and DNA integrity begin to decline after age 35–40.
2. Can older men still father healthy children?
Yes, with proper health and medical monitoring, many men conceive healthy babies.
3. What causes sperm DNA damage?
Oxidative stress, smoking, pollution, and aging cause DNA fragmentation.
4. How to test sperm quality at home?
You can use smartphone-based sperm kits like YO Test or ExSeed.
5. Does sperm quality decline after 40?
Yes, sperm count, motility, and morphology decrease significantly.
6. What is sperm DNA fragmentation?
It’s when the DNA inside sperm cells breaks, reducing fertility potential.
7. Can poor sperm DNA cause miscarriage?
Yes, fragmented sperm DNA increases miscarriage risk.
8. How can I improve sperm quality naturally?
Exercise, avoid smoking, eat antioxidants, and manage stress.
9. How often should men check fertility?
Every 2–3 years after 35, or sooner if planning a baby.
10. Can supplements help sperm health?
Yes, vitamins C, E, zinc, and CoQ10 may improve sperm function.
11. Is male infertility common?
Yes, it contributes to nearly 40–50% of all infertility cases.
12. What lifestyle habits harm sperm?
Smoking, alcohol, poor diet, tight clothes, and lack of sleep.
13. Does stress affect sperm quality?
Yes, stress raises cortisol, lowering testosterone and sperm count.
14. Is late fatherhood safe?
Generally yes, but genetic and developmental risks increase with age.
15. Does exercise improve fertility?
Yes, moderate exercise supports hormone balance and sperm motility.
16. Can obesity affect sperm health?
Yes, excess fat lowers testosterone and increases oxidative stress.
17. How does pollution affect fertility?
Pollutants increase DNA damage and lower sperm motility.
18. Does diet affect sperm?
Yes, nutrients like folate, zinc, and antioxidants improve sperm count.
19. Can men reverse DNA damage in sperm?
Partially, through antioxidants, healthy diet, and medical support.
20. What is the best age for fatherhood?
Ideally between 25–35 years, when sperm quality is highest.
21. Do medications affect sperm?
Certain antibiotics, steroids, and cancer drugs can harm sperm.
22. Can cell phones reduce fertility?
Prolonged heat exposure from phones near genitals may impact sperm.
23. Is sperm freezing an option?
Yes, men can freeze sperm in their 20s–30s for future use.
24. Can diabetes affect sperm?
Yes, it causes hormonal imbalance and DNA damage.
25. What foods boost sperm count?
Spinach, eggs, walnuts, bananas, and tomatoes.
26. How long does sperm stay healthy?
Sperm production takes about 70 days, so changes reflect after 3 months.
27. Can heat exposure harm sperm?
Yes, frequent saunas, hot tubs, or tight underwear can reduce quality.
28. Are older fathers more likely to have daughters?
Some studies suggest slightly higher chances due to chromosomal variation.
29. What vitamins are essential for sperm health?
Vitamins C, E, D, zinc, and selenium.
30. Does caffeine affect sperm?
Moderate caffeine is fine; excess intake may lower motility.
31. Can smoking permanently damage fertility?
Long-term smoking causes irreversible sperm DNA damage.
32. Is alcohol harmful for sperm?
Yes, it reduces testosterone and sperm count.
33. What is a normal sperm count?
Over 15 million sperm per ml is considered healthy.
34. How to know if sperm DNA is fragmented?
Get a DNA fragmentation index (DFI) test at a fertility lab.
35. How does aging affect sperm morphology?
Older sperm often have abnormal shapes, reducing fertilization ability.
36. Does sleep affect sperm health?
Yes, poor sleep lowers testosterone and increases oxidative stress.
37. Are there warning signs of male infertility?
Low libido, erectile issues, and hormonal changes are common signs.
38. Can stress reduce sperm count?
Yes, it can suppress hormones essential for sperm production.
39. What is oxidative stress?
A chemical imbalance in cells that damages sperm DNA.
40. Can yoga help fertility?
Yes, yoga improves circulation, reduces stress, and supports hormones.
41. Can age affect sperm motility?
Yes, sperm movement slows as men age.
42. Do environmental toxins matter?
Yes, pesticides and plastics (BPA) harm sperm health.
43. Can infections reduce fertility?
STIs and prostatitis can damage sperm-producing tissues.
44. How can I boost testosterone naturally?
Weight training, zinc-rich foods, and good sleep help.
45. Can dehydration reduce semen volume?
Yes, water intake affects sperm concentration.
46. Is genetic testing important for older fathers?
Yes, it helps detect hereditary risks early.
47. How long should couples try before seeking help?
After 6–12 months of regular unprotected intercourse.
48. Can fertility improve after quitting smoking?
Yes, sperm quality begins improving within 3 months.
49. What doctor should I consult for male fertility?
An andrologist or fertility specialist.
50. Does sperm age affect pregnancy complications?
Yes, older paternal age can increase miscarriage and disorder risks.









Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!
Leave a Comment