Introduction: Why Everyone’s Talking About Melatonin
In recent years, melatonin supplements have become one of India’s most purchased over-the-counter sleep aids. Whether it’s after a night of scrolling, jet lag, or work stress, many people turn to melatonin tablets hoping for quick relief from insomnia and anxiety-related sleep issues.
But recent research warns that this “natural” hormone might not be as harmless as it seems. Overuse or misuse can disturb your sleep cycle, affect hormone balance, and even worsen anxiety and sleep problems in the long run.
This blog explores how melatonin works, its risks, benefits, and safe alternatives for better sleep.

What Is Melatonin?
Melatonin is a hormone naturally produced by the pineal gland in your brain. It helps regulate your circadian rhythm — your body’s internal clock that tells you when to sleep and wake up.
Melatonin levels rise in the evening as it gets dark and drop in the morning when light returns.
In supplement form, melatonin is used for:
-
Difficulty falling asleep (sleep onset insomnia)
-
Jet lag
-
Shift work sleep disorder
-
Anxiety before surgery or medical tests
However, melatonin pills are often used without medical advice, which can cause more harm than good.
How Melatonin Supplements Work
When you take a melatonin tablet, it signals to your brain that it’s “night time,” helping you feel drowsy. But supplements provide melatonin doses far higher than the body’s natural levels — sometimes 10–20 times more.
This can confuse your brain’s natural rhythm, making you dependent on pills for sleep. In India, these supplements are easily available online or in pharmacies without prescription, increasing the risk of misuse.
Why New Research Warns Caution
A 2024 study published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine found that melatonin use has tripled in the past decade, especially among adults under 40. Researchers discovered:
-
Some over-the-counter melatonin tablets contain up to 400% more melatonin than their labels state.
-
Chronic use can suppress your body’s natural melatonin production.
-
It may disrupt other hormones like cortisol, estrogen, and testosterone.
-
Long-term users reported higher levels of morning grogginess, vivid dreams, and anxiety.
Potential Side Effects of Melatonin
While melatonin is safer than many sleeping pills, it’s not free from side effects. Commonly reported issues include:
-
Daytime sleepiness and fatigue
-
Dizziness and headaches
-
Nausea or stomach cramps
-
Hormonal changes (especially in women)
-
Mood swings and anxiety
-
Nightmares or intense dreams
-
Reduced alertness — dangerous for drivers and shift workers
In teenagers, high doses of melatonin may even delay puberty by interfering with natural hormone cycles.
Melatonin and Anxiety: A Complicated Relationship
While small doses of melatonin can calm anxiety for some people, long-term use may worsen anxiety and sleep patterns. This happens because melatonin affects the same brain chemicals that regulate mood, such as serotonin and GABA.
If you already suffer from generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) or depression, taking melatonin without guidance can make symptoms fluctuate, leading to irritability and restlessness.

Who Should Avoid Melatonin?
You should avoid melatonin supplements or use them only under a doctor’s supervision if you:
-
Are pregnant or breastfeeding
-
Have autoimmune diseases
-
Take antidepressants, blood thinners, or diabetes medication
-
Have hormonal disorders (thyroid, PCOS)
-
Are under 18 years old
Safe Use: If You Still Need Melatonin
If your doctor recommends melatonin, follow these guidelines:
-
Use low doses (0.3–1 mg is often enough; most Indians take 3–10 mg unnecessarily).
-
Take it 30–60 minutes before bedtime.
-
Use for short-term relief only (no longer than 2–3 weeks).
-
Choose trusted brands with verified dosage and purity.
-
Avoid combining it with alcohol, caffeine, or other sleep aids.
Natural Alternatives to Improve Sleep Without Pills
You can train your body to sleep better naturally with these lifestyle changes:
-
Follow a consistent bedtime — go to bed and wake up at the same time daily.
-
Avoid blue light — no screens an hour before bed.
-
Create a calming environment — dim lights, cool temperature, quiet surroundings.
-
Exercise regularly but not too close to bedtime.
-
Eat light dinners and avoid caffeine after 4 PM.
-
Try herbal teas like chamomile or tulsi.
-
Practice mindfulness or deep breathing before bed.
When to See a Doctor
If you’ve been taking melatonin for more than 2 weeks and still struggle to sleep, it’s time to see a general physician or sleep specialist. Persistent insomnia, fatigue, or anxiety could indicate:
-
Sleep apnea
-
Thyroid imbalance
-
Depression or generalized anxiety disorder
-
Medication side effects
Your doctor may suggest blood tests, sleep hygiene counseling, or safe prescription options.
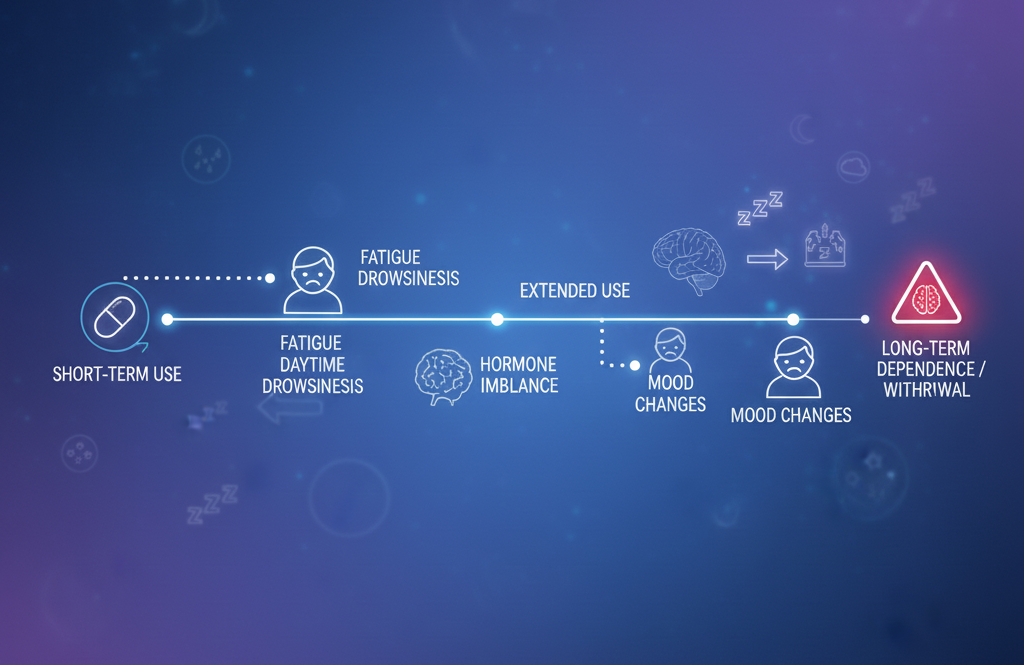
Risks of Long-Term Melatonin Use
Continuous, unsupervised use of melatonin may cause:
-
Dependence — needing higher doses over time
-
Hormone imbalance
-
Mood instability
-
Reduced fertility (in both men and women)
-
Sleep cycle disruption leading to insomnia relapse
Conclusion: Natural Doesn’t Always Mean Safe
Melatonin may seem like a gentle solution for sleepless nights, but it’s still a hormone — and hormones affect your entire body. Used correctly, it can be a short-term ally. But long-term, unsupervised use may cause more harm than good.
If you’re facing sleep or anxiety issues, consult a Quickobook doctor instead of self-medicating. A specialist can help uncover the root cause — whether it’s stress, hormones, or poor habits — and create a personalized plan for healthy, natural sleep.
Quickobook CTAs
Need help with sleep or anxiety?
Book a Quickobook general physician or psychiatrist consultation online today.
Teleconsultation Available: Speak to trusted doctors anytime from home.
Find nearby clinics in your city on Quickobook.in
Get safe, doctor-prescribed sleep solutions — no guesswork, no self-harm.
Frequently Asked Questions (50 Expert Answers)
1. What is melatonin?
Melatonin is a natural hormone produced by the brain’s pineal gland that helps regulate your sleep-wake cycle.
2. Is melatonin safe to take daily?
Short-term use is generally safe, but long-term use without medical supervision can affect hormone balance.
3. How does melatonin help you sleep?
It signals your body that it’s nighttime, helping you fall asleep faster by regulating your internal clock.
4. What is the ideal melatonin dosage for adults?
Most people only need 0.3–1 mg before bed, but many take much higher doses unnecessarily.
5. Can melatonin cause addiction?
Melatonin doesn’t cause physical addiction, but your brain may become psychologically dependent on it.
6. Can melatonin cause anxiety?
Yes, high doses or prolonged use can alter brain chemicals, worsening anxiety in some people.
7. Does melatonin affect hormones?
Yes, it can impact reproductive and stress hormones like estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol.
8. Can teenagers take melatonin?
It’s not recommended without a doctor’s advice because it can interfere with puberty and growth.
9. Is melatonin safe during pregnancy?
No, pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid it unless prescribed by a doctor.
10. How long does melatonin take to work?
Usually, it starts working within 30 to 60 minutes after taking it.
11. Can melatonin help with jet lag?
Yes, it can help reset your sleep cycle during travel across time zones when used properly.
12. Can melatonin help anxiety-related insomnia?
It may temporarily help, but addressing the root cause of anxiety is more effective long-term.
13. What are the side effects of melatonin?
Common side effects include headache, dizziness, nausea, and daytime sleepiness.
14. Can melatonin cause nightmares?
Yes, vivid dreams or nightmares are a known side effect due to REM cycle alteration.
15. Can you overdose on melatonin?
While rarely fatal, too much melatonin can cause confusion, low blood pressure, and extreme drowsiness.
16. Does melatonin interfere with other medications?
Yes, it can interact with antidepressants, blood thinners, and diabetes medicines.
17. How long should I take melatonin?
Limit use to 2–3 weeks unless advised otherwise by your doctor.
18. Can melatonin cause depression?
Some people report mood changes or worsening depression with long-term use.
19. Can melatonin affect fertility?
Yes, long-term high doses may impact fertility in both men and women.
20. Can I take melatonin with alcohol?
No, alcohol can reduce its effectiveness and increase side effects.
21. Does melatonin help with shift work sleep disorder?
It can help temporarily but should not replace good sleep hygiene or medical supervision.
22. Is melatonin suitable for elderly people?
Older adults can use low doses safely under medical guidance.
23. Does melatonin lower blood pressure?
It can lower blood pressure slightly, so caution is needed for people on BP medication.
24. Can melatonin cause morning grogginess?
Yes, taking too much or taking it too late can cause next-day drowsiness.
25. Can melatonin treat chronic insomnia?
It may help short-term, but behavioral therapy and lifestyle changes are better long-term solutions.
26. Does melatonin help with migraines?
Some studies suggest it may reduce migraine frequency, but more research is needed.
27. Can children take melatonin?
Only under pediatric supervision for specific sleep disorders.
28. Does melatonin affect thyroid function?
It may influence thyroid hormone production, so use cautiously if you have thyroid disease.
29. Can I take melatonin with antidepressants?
Consult your doctor first; combining them can cause unpredictable effects on mood and sleep.
30. Is melatonin a natural or synthetic supplement?
The body produces natural melatonin, but most supplements are synthetically made.
31. Can melatonin make you feel anxious or jittery?
Yes, especially if you already struggle with anxiety or take it in high doses.
32. Does melatonin help with PTSD-related sleep issues?
It may help temporarily but should be part of a broader treatment plan.
33. Can melatonin affect menstrual cycles?
Yes, it may alter reproductive hormones, affecting menstrual regularity.
34. Can melatonin improve REM sleep?
It can increase REM sleep duration, but excessive doses may disrupt sleep quality.
35. Is melatonin safe for diabetic patients?
Use with caution — it may interfere with blood sugar control.
36. Can melatonin help after night shifts?
It can help realign your sleep schedule, but lifestyle management is equally important.
37. What foods naturally boost melatonin?
Cherries, milk, bananas, and oats naturally contain melatonin or its precursors.
38. Is melatonin approved by the Indian drug authority?
Yes, it’s available as an over-the-counter supplement, but regulation is limited.
39. How does melatonin differ from sleeping pills?
Melatonin regulates sleep hormones, while sleeping pills act as sedatives.
40. Can melatonin cause weight gain?
There’s no direct link, but poor sleep or hormonal changes may contribute to weight fluctuation.
41. Does melatonin affect dreams?
Yes, many users experience more vivid or intense dreams.
42. Can melatonin help people with ADHD sleep better?
It may help, but only under medical advice.
43. Can melatonin reduce stress levels?
It may calm your nervous system slightly, but it’s not a treatment for chronic stress.
44. Is it safe to buy melatonin online?
Only purchase from verified pharmacies or healthcare platforms like Quickobook for safety.
45. What is the best time to take melatonin?
Take it 30–60 minutes before your regular bedtime.
46. Does melatonin interact with caffeine?
Yes, caffeine can block melatonin’s sleep-promoting effects.
47. How can I stop taking melatonin safely?
Gradually reduce dosage and replace it with sleep hygiene practices.
48. Can melatonin be used during menopause?
It may ease mild sleep problems, but consult a gynecologist first.
49. What are natural alternatives to melatonin?
Chamomile tea, magnesium, ashwagandha, and mindfulness can promote natural sleep.
50. When should I see a doctor about my sleep problems?
If sleep issues last more than 2 weeks or affect your daily life, consult a Quickobook doctor for proper evaluation.









Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!
Leave a Comment