Introduction: Type 2 Diabetes — India’s Growing Health Challenge
Type 2 diabetes is one of the most common chronic diseases in India and worldwide. It affects how your body uses glucose (sugar) for energy. When the body becomes insulin resistant or fails to produce enough insulin, glucose builds up in the blood — leading to long-term complications.
According to the Indian Council of Medical Research, more than 100 million Indians live with diabetes. While it’s a lifelong condition, Type 2 diabetes can be managed — and sometimes even reversed — through lifestyle changes, timely treatment, and healthy eating for diabetics.
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
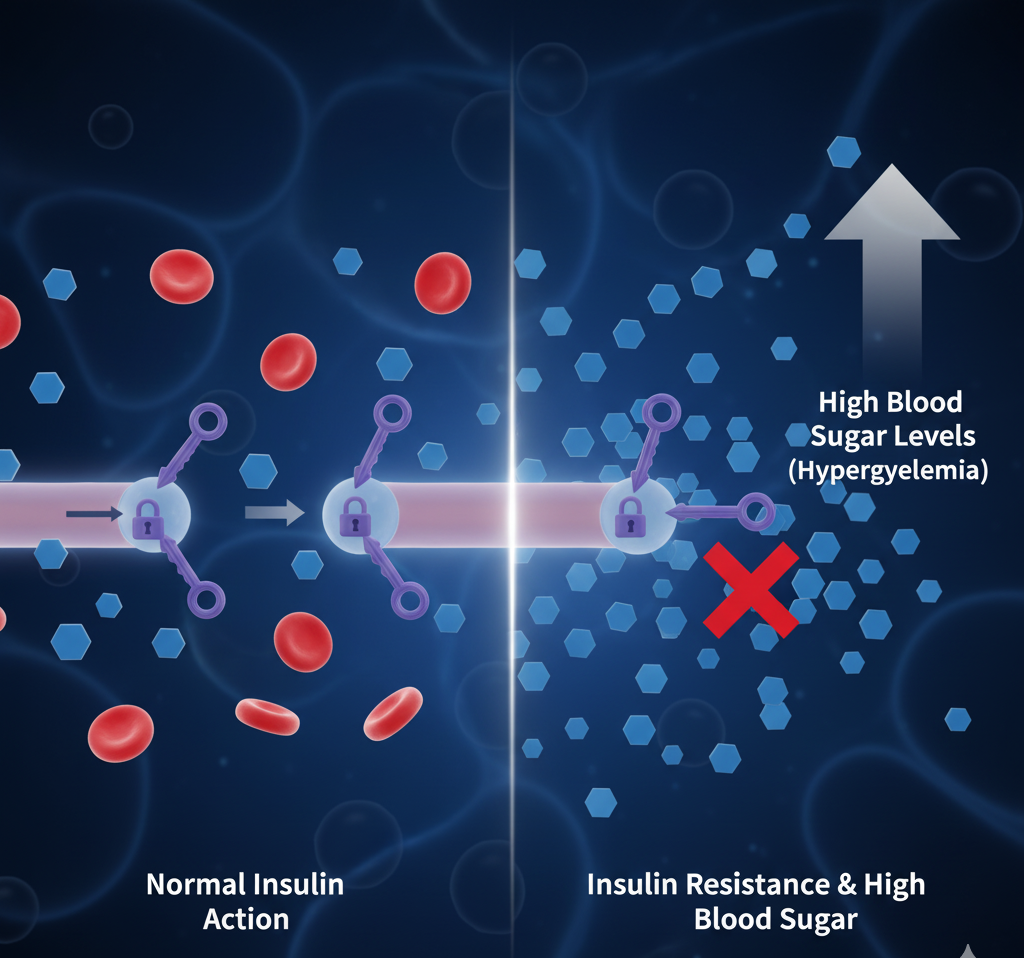
Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder where your body either resists insulin (the hormone that regulates sugar) or doesn’t produce enough of it.
Unlike Type 1 diabetes, which usually develops early in life and requires insulin injections, Type 2 is more common in adults — often due to poor diet, inactivity, or obesity. However, it’s now rising rapidly among younger people due to sedentary lifestyles.
How Insulin Works
Insulin is produced by the pancreas. It helps move sugar from your blood into your cells for energy.
In Type 2 diabetes:
-
The body doesn’t respond properly to insulin (insulin resistance).
-
The pancreas struggles to produce enough insulin.
-
Blood sugar levels rise, leading to hyperglycemia.
Over time, this affects the heart, kidneys, eyes, and nerves.
Common Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Many people have no obvious symptoms in the early stages. However, look out for these warning signs:
-
Frequent urination, especially at night
-
Increased thirst and dry mouth
-
Constant hunger or fatigue
-
Unexplained weight loss or gain
-
Blurred vision
-
Slow-healing wounds
-
Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
-
Frequent infections (especially skin or urinary tract)
If you experience these signs, get your blood glucose levels checked promptly.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause isn’t always clear, but several factors increase risk:
-
Family history of diabetes
-
Overweight or obesity
-
Physical inactivity
-
Unhealthy eating habits (high sugar, refined carbs, or processed food)
-
High blood pressure or cholesterol
-
Gestational diabetes during pregnancy
-
Age above 40 years
-
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women

Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes
Doctors use several tests to confirm diabetes:
-
Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS): ≥126 mg/dL indicates diabetes.
-
Postprandial (PP) Test: ≥200 mg/dL after 2 hours.
-
HbA1c Test: Average blood sugar over 3 months; ≥6.5% suggests diabetes.
-
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Checks body’s sugar-handling ability.
Regular screening after age 30 is crucial — especially if you’re overweight or have family history.
Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes
Managing Type 2 diabetes requires a comprehensive approach involving diet, exercise, and medication.
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
-
Walk or exercise at least 30 minutes daily.
-
Maintain a healthy weight.
-
Sleep 7–8 hours daily and manage stress.
2. Medications:
-
Metformin: First-line drug that reduces glucose production in the liver.
-
SGLT2 inhibitors, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 analogs – used as per doctor’s advice.
-
Insulin therapy: Required in advanced cases.
3. Regular Monitoring:
Keep track of fasting glucose, post-meal sugar, and HbA1c levels.
4. Routine Check-ups:
See an endocrinologist or diabetologist every 3–6 months to prevent complications.
Healthy Eating for Diabetics
A balanced diet is the most powerful way to control blood sugar naturally.
Foods to include:
-
Whole grains: Brown rice, oats, millets, quinoa.
-
Vegetables: Spinach, broccoli, bottle gourd, bitter gourd.
-
Fruits: Apples, guava, papaya, berries (in moderation).
-
Protein sources: Lentils, eggs, tofu, and fish.
-
Healthy fats: Olive oil, almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds.
Foods to avoid:
-
White rice, maida, and sugary snacks.
-
Sodas, juices, and sweetened beverages.
-
Fried or processed foods.
-
Excessive red meat.
Smart tips:
-
Eat smaller, frequent meals every 3–4 hours.
-
Avoid skipping breakfast.
-
Drink 2–3 liters of water daily.
Complications of Type 2 Diabetes
If untreated, diabetes can lead to:
-
Heart disease or stroke
-
Kidney failure (diabetic nephropathy)
-
Eye damage (retinopathy)
-
Nerve damage (neuropathy)
-
Foot ulcers or amputations
-
Increased risk of infections
Regular monitoring and preventive care can minimize these risks.
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
You can prevent or delay onset through small, consistent steps:
-
Exercise regularly (walking, cycling, yoga).
-
Eat fiber-rich, low-sugar foods.
-
Maintain a healthy BMI.
-
Manage stress with meditation or breathing exercises.
-
Get regular check-ups and sugar tests.

When to See a Doctor
You should consult a diabetologist or endocrinologist if you experience:
-
Fatigue and frequent urination
-
Vision changes
-
Foot pain, numbness, or wounds that don’t heal
-
Sudden weight loss
Quickobook makes it easy to book diabetes specialists and lab tests online for early detection and control.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes doesn’t have to control your life — with the right habits, you can manage it successfully. A healthy lifestyle, mindful eating, and regular check-ups are your strongest tools.
Focus on healthy eating for diabetics, stay active, and stay consistent. Remember, every small step — from skipping sugar to walking daily — brings your blood sugar closer to normal.
Quickobook CTA
Book an appointment with a diabetologist or endocrinologist on Quickobook for sugar testing and personalized management plans.
Visit Quickobook.com for trusted doctors, verified reviews, and easy online scheduling.
50 FAQs: Type 2 Diabetes
Q1. What is Type 2 diabetes?
A condition where the body doesn’t use insulin properly, causing high blood sugar.
Q2. How is it different from Type 1 diabetes?
Type 1 requires insulin for life; Type 2 can often be managed with diet and lifestyle.
Q3. What causes Type 2 diabetes?
Genetics, obesity, poor diet, and inactivity are major causes.
Q4. Can Type 2 diabetes be cured?
Not cured, but it can be reversed with healthy habits and weight control.
Q5. What is insulin resistance?
When the body’s cells don’t respond well to insulin.
Q6. What are normal blood sugar levels?
Fasting: below 100 mg/dL; Post-meal: below 140 mg/dL.
Q7. What is the HbA1c test?
It shows your average blood sugar over the last 3 months.
Q8. Can stress raise blood sugar?
Yes, stress hormones increase glucose production.
Q9. Can thin people get Type 2 diabetes?
Yes, especially if they have poor diet or family history.
Q10. Can it be prevented?
Yes, through regular exercise and healthy eating.
Q11. What are the first symptoms?
Frequent urination, thirst, fatigue, and blurred vision.
Q12. Is diabetes hereditary?
Family history increases risk but lifestyle matters more.
Q13. What is diabetic neuropathy?
Nerve damage caused by high blood sugar.
Q14. What foods lower blood sugar?
Bitter gourd, fenugreek, flaxseed, and leafy greens.
Q15. Can skipping meals cause sugar spikes?
Yes, it can cause imbalance and hypoglycemia later.
Q16. How often should I check my sugar?
Daily if advised, or weekly for stable patients.
Q17. Can fruits be eaten by diabetics?
Yes, low-GI fruits like apple, guava, and papaya are safe.
Q18. What exercises help?
Brisk walking, cycling, swimming, and yoga.
Q19. Can I reverse diabetes naturally?
Weight loss, healthy eating, and physical activity can normalize sugar levels.
Q20. What is the best breakfast for diabetics?
Oats, boiled eggs, multigrain toast, and fresh fruits.
Q21. Can diabetes cause fatigue?
Yes, because cells can’t efficiently use glucose for energy.
Q22. Can coffee raise sugar levels?
Unsweetened coffee in moderation is safe.
Q23. What are diabetic complications?
Heart, kidney, eye, and nerve damage.
Q24. Can stress management help?
Yes, meditation and deep breathing lower sugar levels.
Q25. Can diabetes cause vision loss?
Yes, uncontrolled diabetes can cause retinopathy.
Q26. What are good snacks for diabetics?
Nuts, roasted chickpeas, and fruit salads.
Q27. Can alcohol affect sugar levels?
Yes, it can cause spikes or drops — avoid heavy drinking.
Q28. Can fasting improve sugar control?
Short-term fasting may help but consult your doctor first.
Q29. Is brown rice better than white rice?
Yes, it has more fiber and a lower glycemic index.
Q30. Can diabetes cause skin problems?
Yes, poor circulation may cause infections and dryness.
Q31. What is a diabetic foot?
Injury or ulcer in the foot due to nerve damage.
Q32. Can sleep affect blood sugar?
Yes, poor sleep increases insulin resistance.
Q33. Can Type 2 diabetes cause weight loss?
Yes, due to inefficient glucose usage.
Q34. How often should I visit a doctor?
Every 3 months for sugar and HbA1c checks.
Q35. What is the role of Metformin?
It reduces liver glucose production and improves insulin sensitivity.
Q36. Can I take herbal medicines?
Only with doctor’s approval — some may interfere with medication.
Q37. Is yogurt good for diabetics?
Yes, low-fat yogurt helps digestion and controls sugar.
Q38. Can dehydration raise sugar levels?
Yes, it concentrates glucose in the blood.
Q39. What is a low-GI diet?
A diet that includes foods releasing sugar slowly.
Q40. Is honey better than sugar?
No, it also raises blood sugar quickly.
Q41. Can diabetes cause kidney disease?
Yes, prolonged high sugar damages kidneys.
Q42. How does exercise help?
It improves insulin sensitivity and lowers sugar.
Q43. Can diabetics donate blood?
Yes, if sugar levels are controlled and no complications exist.
Q44. Can I eat rice?
Yes, in moderation — pair with fiber and protein.
Q45. Can diabetes affect pregnancy?
Yes, needs special monitoring (gestational diabetes risk).
Q46. What is diabetic ketoacidosis?
A serious condition when blood acid levels rise — seek emergency help.
Q47. Can cinnamon help control diabetes?
It may help improve insulin sensitivity.
Q48. How to handle low sugar levels (hypoglycemia)?
Eat a quick snack like glucose tablets or fruit juice.
Q49. What’s the cost of diabetes tests in India?
Basic sugar tests ₹150–₹400; HbA1c ₹500–₹800.
Q50. Where can I book a diabetes check-up?
Book lab tests or doctor visits at Quickobook.com.










Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!
Leave a Comment