Introduction
Women’s health in India is shaped by biology, lifestyle, culture, and access to healthcare. From menstrual issues to hormonal conditions, pregnancy care to menopause, and cancers to everyday nutritional deficiencies, Indian women experience unique health challenges throughout their lives. Early awareness saves lives. Understanding the basics of reproductive health, preventive care, symptoms to watch for, and when to seek medical help can empower every woman to take charge of her well-being.
This guide explains the most important women’s health issues in India in simple, clear language—covering what they are, why they happen, symptoms to notice, and available treatments. The primary focus remains improving women’s health and reproductive health awareness across all age groups.
Overview of Women’s Health Issues in India
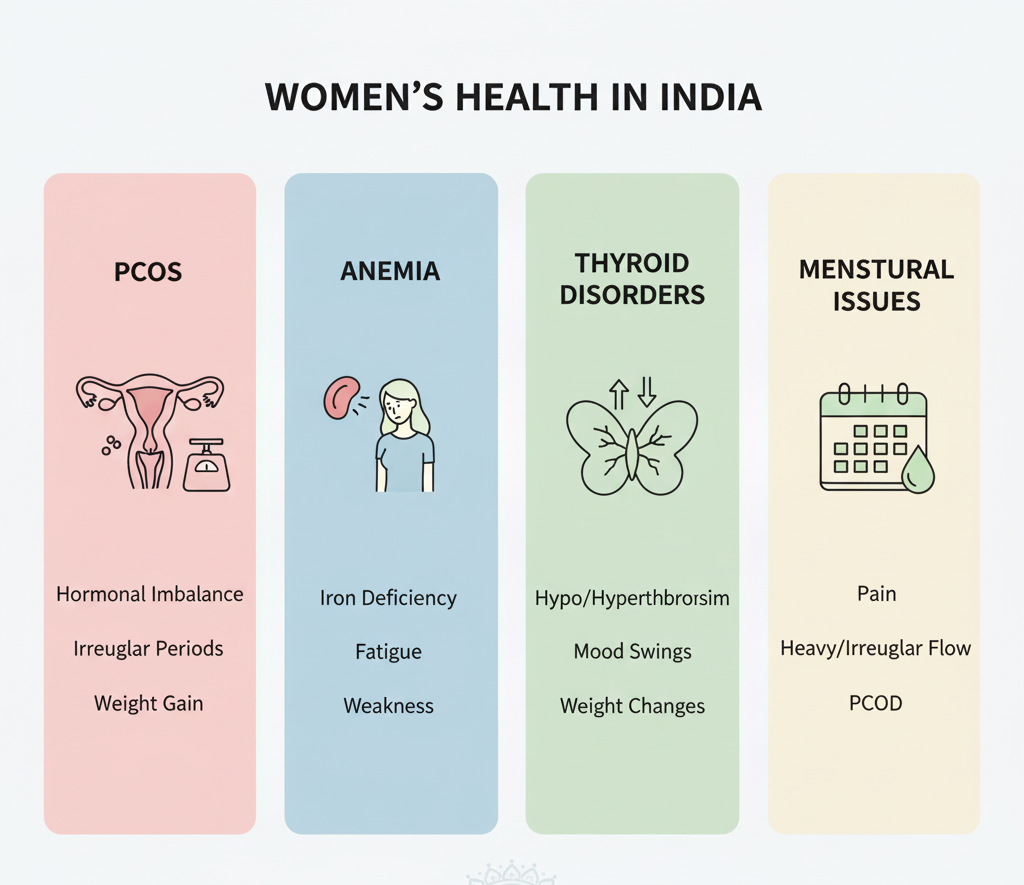
Women in India commonly face health challenges such as PCOS, anemia, thyroid disorders, menstrual irregularities, infertility, endometriosis, pregnancy complications, menopausal symptoms, breast cancer, cervical cancer, UTIs, and lifestyle-related conditions. Many of these issues go unnoticed because women often ignore symptoms, lack awareness, or hesitate to discuss reproductive health openly.
Addressing women’s health starts with education, regular check-ups, and seeking timely medical care.
Common Women’s Health Issues
PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)
A hormonal condition causing irregular periods, acne, weight gain, facial hair, mood changes, and difficulty conceiving. PCOS is rising rapidly among Indian women due to stress, sedentary lifestyles, and hormonal imbalance.
Menstrual Problems
Irregular cycles, heavy bleeding, painful periods, and missed periods are extremely common. These may be linked to anemia, hormonal imbalance, stress, thyroid disorders, or reproductive health issues.
Breast and Cervical Cancer
Breast cancer is now the most common cancer among Indian women. Cervical cancer remains widespread due to limited screening and low HPV vaccination rates.
Anemia
More than 50% of Indian women suffer from anemia, mainly due to iron deficiency, poor diet, and heavy periods.
Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are common and affect weight, mood, periods, energy levels, and fertility.
Infertility
A growing concern, caused by PCOS, age, fibroids, endometriosis, infections, lifestyle habits, or male factors.
Endometriosis
A painful condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus.
Pregnancy-Related Issues
Gestational diabetes, hypertension, anemia, miscarriage risk, and infections must be monitored closely.
UTI (Urinary Tract Infections)
Painful urination, burning, increased frequency, and lower abdominal discomfort are common symptoms.
Menopause and Perimenopause
Hot flashes, mood swings, sleep problems, bone loss, and hormonal changes affect quality of life.
Causes of Women’s Health Issues
Women’s health conditions arise from a range of factors:
● Hormonal imbalance
● Genetics
● Poor nutrition
● Sedentary lifestyle
● Stress and lack of rest
● Early or late pregnancies
● Reproductive tract infections
● Poor menstrual hygiene
● Environmental factors
● Aging and menopause
● Lack of screening and preventive care
● Cultural hesitation to seek timely medical help
Symptoms Women Should Never Ignore
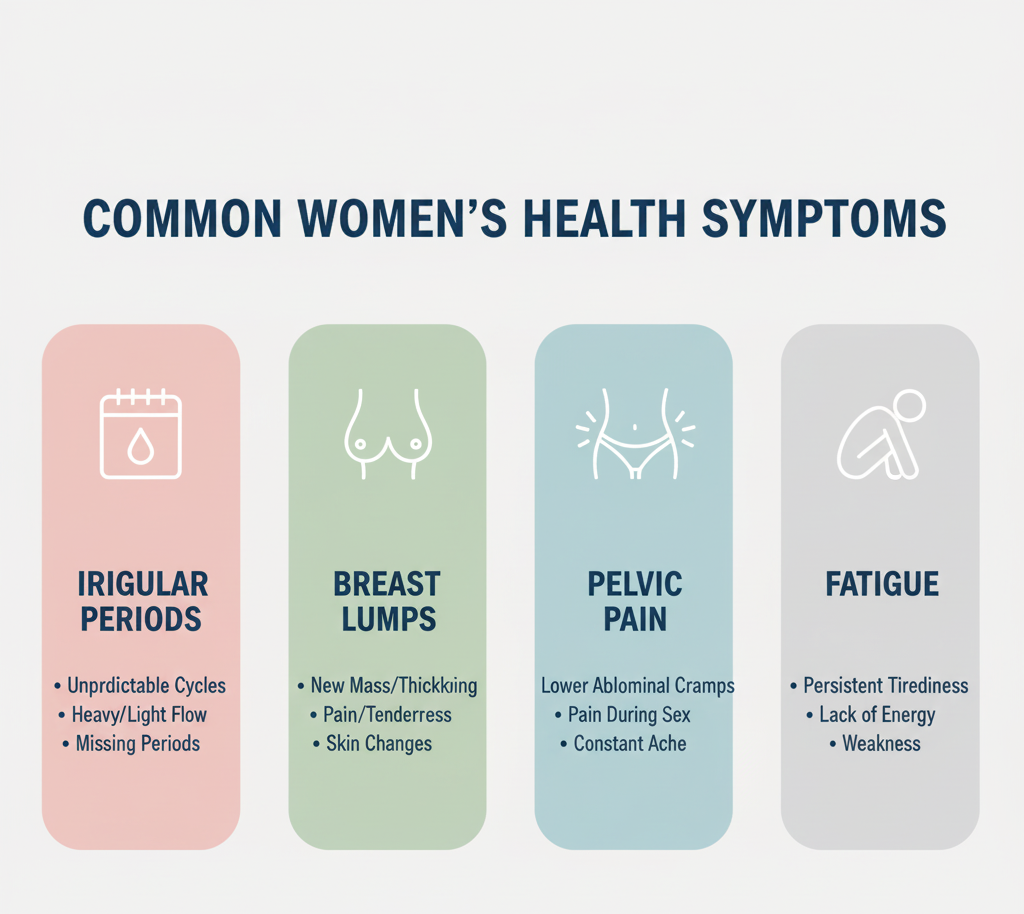
● Irregular periods
● Severe cramps
● Very heavy or very light bleeding
● Sudden weight gain or loss
● Breast lumps or nipple discharge
● Pelvic pain
● Pain during sex
● Vaginal itching or unusual discharge
● Excessive hair growth or hair loss
● Unexplained fatigue
● Frequent urination or burning sensation
● Persistent lower back or abdominal pain
● Mood changes or depression
● Hot flashes or night sweats
Any persistent symptom deserves medical attention.
Diagnosis of Women’s Health Conditions
Doctors use a combination of:
● Physical examination
● Pelvic exam
● Blood tests (hormones, thyroid, sugar levels, anemia profile)
● Ultrasound
● Mammography
● Pap smear
● Urine analysis
● Hormonal panels
● STD/STI testing
● Fertility testing (AMH, ovulation tests)
Early diagnosis helps prevent complications.
ALSO READ: Most Common Lifestyle Diseases In India
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the condition but may include:
● Lifestyle changes
● Hormonal medicines
● Pain relief medication
● Antibiotics for infections
● Supplements like iron, vitamin D, calcium
● Thyroid medication
● Fertility treatments
● Surgery (fibroids, cysts, endometriosis)
● Cancer therapies (chemo, radiation, surgery)
● Counseling and mental health support
Never start medication without a doctor’s advice. Dosage varies for each person.
Lifestyle Tips for Better Women’s Health
● Eat iron-rich and protein-rich foods.
● Exercise at least 30 minutes daily.
● Maintain healthy weight.
● Stay hydrated.
● Sleep 7–8 hours.
● Reduce stress through meditation or yoga.
● Limit junk food, sugary drinks, alcohol, and smoking.
● Practice safe sex.
● Maintain menstrual hygiene.
● Avoid self-medication.
● Go for routine check-ups.
Prevention Strategies Every Woman Should Follow
● Regular gynecological exams
● Yearly Pap smear
● HPV vaccination
● Breast self-exam every month
● Screening after age 40 for breast cancer
● Balanced diet
● Healthy BMI
● Safe pregnancy planning
● Timely treatment of infections
● Early management of hormonal issues
When to See a Doctor

Consult a gynaecologist immediately if you notice:
● Irregular cycles for more than 3 months
● Very painful periods
● Excessive bleeding
● Breast lumps
● Pelvic pain
● Difficulty conceiving
● Severe mood changes
● Post-menopausal bleeding
● Painful urination
● Persistent fatigue
● Symptoms that interfere with daily life
Quickobook allows you to book verified doctors instantly when needed.
Risks and Complications if Issues Are Ignored
● Infertility
● Anemia complications
● Miscarriages
● Chronic pelvic pain
● Hormonal imbalance
● Diabetes or thyroid worsening
● Cervical or breast cancer progression
● Pregnancy-related risks
● Bone weakness (osteoporosis)
● Severe infections
● Emotional and mental health concerns
Early care prevents long-term health problems.
50 FAQs (Short, Simple Answers)
Q1. What is the most common women’s health issue in India?
A1. Anemia, PCOS, menstrual problems, and thyroid disorders are very common.
Q2. How often should women get a health check-up?
A2. Once a year is ideal for routine women’s health screening.
Q3. What is reproductive health?
A3. It includes menstrual health, fertility, pregnancy care, and sexual wellness.
Q4. When should a girl first visit a gynaecologist?
A4. Anytime after age 13–15 or when menstrual problems begin.
Q5. Can stress affect periods?
A5. Yes, stress can delay or disturb menstrual cycles.
Q6. What is a normal menstrual cycle length?
A6. Between 21 and 35 days.
Q7. What causes irregular periods?
A7. PCOS, thyroid issues, stress, weight changes, and hormonal imbalance.
Q8. How can I reduce period pain?
A8. Heat pads, hydration, light exercise, and prescribed medicines help.
Q9. Are heavy periods serious?
A9. Yes, they may indicate anemia, fibroids, or hormonal imbalance.
Q10. What is PCOS?
A10. A hormonal disorder affecting periods, fertility, and metabolism.
Q11. Is PCOS curable?
A11. Not fully, but symptoms can be managed with lifestyle and treatment.
Q12. Can PCOS cause infertility?
A12. Yes, it can affect ovulation but is treatable.
Q13. What is endometriosis?
A13. A condition where uterine lining grows outside the uterus causing pain.
Q14. Can thyroid problems affect periods?
A14. Yes, they cause irregular cycles and fertility issues.
Q15. How can I detect breast cancer early?
A15. Do monthly self-exams and screening after 40.
Q16. What is a breast self-exam?
A16. Checking for lumps, changes, or pain at home.
Q17. Does a lump always mean cancer?
A17. No, many lumps are benign but should be checked.
Q18. What is cervical cancer screening?
A18. A Pap smear detects early changes.
Q19. Who should get a Pap smear?
A19. All sexually active women aged 21–65.
Q20. Is HPV vaccination safe?
A20. Yes, it prevents most cervical cancers.
Q21. What causes urinary infections?
A21. Poor hygiene, dehydration, and bacterial entry.
Q22. How to prevent UTI?
A22. Drink water, maintain hygiene, empty bladder regularly.
Q23. What causes infertility in women?
A23. PCOS, age, thyroid issues, infections, endometriosis.
Q24. Can infertility be treated?
A24. Yes, through medication, lifestyle changes, or IVF.
Q25. How much water should women drink daily?
A25. Around 2–2.5 litres.
Q26. What foods help women’s health?
A26. Iron, calcium, protein, fruits, and whole grains.
Q27. What causes anemia in women?
A27. Heavy periods and low iron intake.
Q28. Signs of anemia?
A28. Fatigue, pale skin, dizziness.
Q29. How to treat anemia?
A29. Iron supplements and diet changes.
Q30. What is menopause?
A30. Natural end of periods, usually around age 45–50.
Q31. Symptoms of menopause?
A31. Hot flashes, mood swings, dryness.
Q32. Can menopause be treated?
A32. Symptoms can be eased with medicines and lifestyle care.
Q33. What is reproductive health care?
A33. Period, fertility, pregnancy, and sexual wellness support.
Q34. When should I test for pregnancy?
A34. After a missed period.
Q35. What is a fibroid?
A35. A non-cancerous growth in the uterus.
Q36. Can fibroids cause pain?
A36. Yes, pelvic pain and heavy bleeding.
Q37. What causes vaginal discharge?
A37. Natural cycles or infections.
Q38. When is discharge abnormal?
A38. When foul-smelling, itchy, or coloured.
Q39. Can infections affect fertility?
A39. Yes, untreated infections may damage the reproductive tract.
Q40. Why do women gain weight easily?
A40. Hormonal changes and slower metabolism.
Q41. Can lifestyle changes improve women’s health?
A41. Yes, diet and exercise play a major role.
Q42. Does smoking affect women’s health?
A42. Yes, it increases cancer and infertility risks.
Q43. What screening is needed after 40?
A43. Mammogram, thyroid tests, sugar tests, bone health checks.
Q44. Can women lift weights safely?
A44. Yes, strength training is beneficial.
Q45. What is gestational diabetes?
A45. Diabetes that occurs during pregnancy.
Q46. Can pregnancy be planned safely?
A46. Yes, with preconception counselling.
Q47. How often should women check thyroid levels?
A47. Once a year or as advised.
Q48. What vitamin do women commonly lack?
A48. Vitamin D and B12.
Q49. Can mental health affect physical health?
A49. Yes, stress affects hormones and immunity.
Q50. When should I see a gynaecologist urgently?
A50. Severe pain, heavy bleeding, breast lumps, fever, or unusual symptoms.
Conclusion
Women’s health is a lifelong journey shaped by physical, emotional, and reproductive factors. Awareness and timely care can prevent most complications. By understanding symptoms, tracking health changes, prioritizing preventive check-ups, and seeking medical help without hesitation, every woman in India can protect her well-being at every age.
Quickobook CTA
Need guidance on menstrual problems, fertility, PCOS, pregnancy, or any women’s health concern?
Book a verified gynaecologist on Quickobook today.
Fast appointments, trusted doctors, and safe care — all in one place.
Disclaimer
This blog is for educational purposes only. It does not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified doctor for personalised care.










Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!
Leave a Comment