Introduction
Dementia is a condition that affects memory, thinking, behaviour, and daily functioning. In India, the number of dementia cases is rising due to increased life expectancy, limited awareness, and lifestyle changes. Recognising the early signs of dementia is essential for timely diagnosis and support.
This guide offers Indian families simple and clear information while focusing on dementia and brain health.
What Is Dementia?
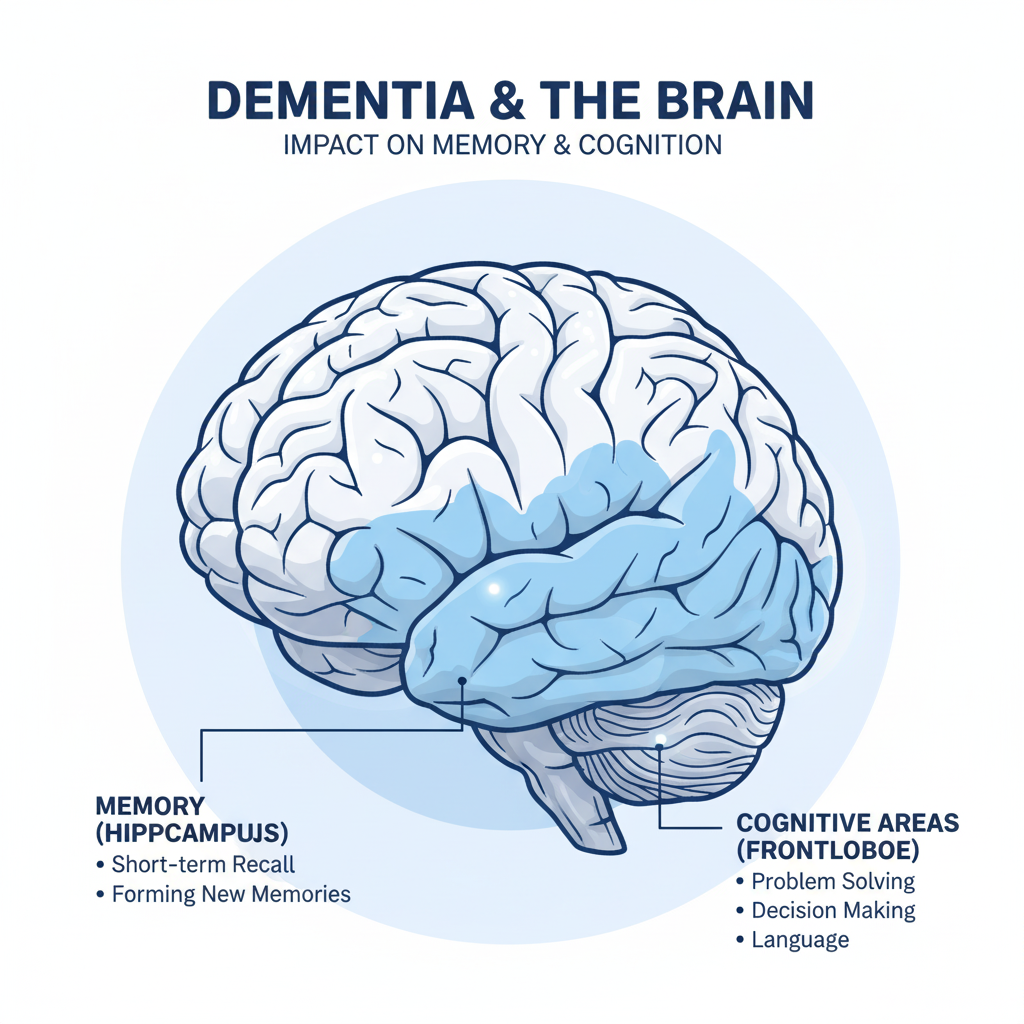
Dementia refers to a set of symptoms that affect brain function. It leads to problems with remembering, thinking, decision-making, and daily activities. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia.
Early Signs of Dementia
Memory Problems
One of the earliest symptoms is memory loss that affects everyday life. People may forget recent conversations, repeat questions, misplace items, or forget the names of familiar people.
Difficulty Planning or Solving Problems
Managing money, cooking, understanding bills, or planning daily tasks becomes challenging.
Confusion About Time or Place
People may forget dates, seasons, or where they are, even in familiar places.
Trouble Completing Familiar Tasks
Simple activities like cooking, using a mobile phone, or driving to known locations may feel confusing.
Problems With Speaking or Understanding
They may struggle to find words, repeat sentences, or forget the flow of a conversation.
Poor Judgment
Unexpected decisions such as giving money to strangers, choosing wrong clothes for weather, or risky behaviours may occur.
Mood or Personality Changes
People may become anxious, irritated, withdrawn, or suddenly depressed.
Difficulty Recognising People or Objects
A strong indicator of Alzheimer’s-related dementia.
Causes of Dementia
Dementia may develop due to several factors such as:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
-
Stroke or vascular issues
-
Parkinson’s disease
-
Head injuries
-
Vitamin B12 deficiency
-
Thyroid disorders
-
Infections
ALSO READ: Mental Health Awareness In India
Risk Factors
Factors increasing the risk include:
-
Age above 60
-
Family history
-
Smoking
-
High blood pressure
-
Diabetes
-
High cholesterol
-
Obesity
-
Poor sleep
-
Excessive alcohol use
-
Lack of mental activity
Diagnosis of Dementia

Doctors may use:
-
Memory tests (MMSE, MoCA)
-
Blood tests (thyroid, vitamin levels)
-
Brain scans (MRI, CT)
-
Behavioural assessments
A neurologist or psychiatrist usually confirms the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Dementia cannot be completely cured, but symptoms can be managed.
Medication
Doctors may prescribe:
-
Donepezil
-
Rivastigmine
-
Memantine
Only a doctor can decide dosage.
Therapies
-
Cognitive therapy
-
Behavioural counselling
-
Speech therapy
-
Physiotherapy
Daily Support
-
Use of reminder apps or notes
-
Safe home environment
-
Maintaining a structured routine
Improving Brain Health
Steps to support brain health include:
-
Daily exercise
-
Healthy diet rich in nuts, seeds, fruits, vegetables
-
Mental activities like reading or puzzles
-
Social interaction
-
Good sleep habits
-
Avoiding smoking and alcohol
Prevention
You may reduce dementia risk by:
-
Managing BP, cholesterol, diabetes
-
Exercising regularly
-
Eating a balanced diet
-
Staying mentally active
-
Maintaining good sleep quality
When to See a Doctor

Consult a neurologist if you notice:
-
Increasing forgetfulness
-
Difficulty recognising people
-
Sudden mood or behaviour changes
-
Repeated confusion
-
Trouble speaking or understanding
-
Difficulty performing familiar tasks
Early diagnosis helps slow progression.
Complications
Untreated dementia may lead to:
-
Loss of independence
-
Falls and injuries
-
Malnutrition or dehydration
-
Wandering behaviour
-
Depression
-
Caregiver stress
Conclusion
Dementia is a progressive condition, but early recognition and support can improve life quality. By promoting brain health, seeking medical help early, and making lifestyle changes, families can ensure better care and comfort for their loved ones.
Quickobook CTA
Concerned about symptoms of memory loss or dementia?
Book a trusted neurologist on Quickobook today.
Teleconsultation available across India.
Fast, reliable, and easy appointments.
Disclaimer
This blog provides general information and is not a substitute for medical advice. Always consult a certified doctor for diagnosis or treatment.
50 FAQs
Q1. What is the earliest sign of dementia?
A: Memory loss that affects daily life.
Q2. Does dementia affect only older adults?
A: Mostly, but early-onset dementia can occur before age 60.
Q3. Is dementia the same as Alzheimer’s?
A: Alzheimer’s is a type of dementia, not the same condition.
Q4. Can dementia be cured?
A: No, it can be managed but not cured.
Q5. Is dementia hereditary?
A: Family history increases risk but does not guarantee dementia.
Q6. Can stress cause dementia?
A: Chronic stress harms brain health but is not a direct cause.
Q7. Can dementia appear suddenly?
A: Symptoms usually develop slowly.
Q8. Do all dementia patients lose memory?
A: Yes, but not all lose it at the same rate.
Q9. When should someone see a doctor?
A: When memory loss affects daily routine.
Q10. Can vitamin B12 deficiency mimic dementia?
A: Yes, and it can be reversible.
Q11. What age does dementia usually start?
A: After age 60.
Q12. Can thyroid problems cause memory loss?
A: Yes, hypothyroidism affects concentration and memory.
Q13. Can dementia be reversed if caught early?
A: Some causes are reversible; others are not.
Q14. Is mood change an early symptom?
A: Yes, irritability and anxiety are common.
Q15. Can dementia cause speech problems?
A: Yes, trouble finding words is common.
Q16. Does dementia affect sleep?
A: Many experience sleep disturbances.
Q17. Can dementia cause wandering?
A: Yes, due to confusion.
Q18. Do people with dementia forget family members?
A: In later stages, recognition declines.
Q19. Does alcohol increase dementia risk?
A: Heavy drinking is a major risk factor.
Q20. Can brain exercises help?
A: Yes, they support brain health.
Q21. Does dementia worsen quickly?
A: The speed varies from person to person.
Q22. Can infections cause sudden confusion?
A: Yes, especially UTIs in older adults.
Q23. Can dementia patients live alone?
A: Early stage—maybe; later stages—no.
Q24. Is MRI necessary for diagnosis?
A: Helpful but not always required.
Q25. Can dehydration cause confusion?
A: Yes, especially in seniors.
Q26. Are women more likely to develop dementia?
A: Yes, due to longer lifespan.
Q27. Is dementia common in India?
A: Yes, cases are increasing.
Q28. Can dementia cause balance problems?
A: Yes, certain types affect coordination.
Q29. Does dementia cause anger or aggression?
A: Yes, frustration may lead to aggression.
Q30. Can diet improve brain health?
A: A balanced diet supports memory and focus.
Q31. Does dementia affect vision?
A: It affects visual understanding, not eyesight.
Q32. Can poor sleep increase dementia risk?
A: Yes, quality sleep supports brain health.
Q33. Is dementia a mental illness?
A: No, it is a neurological condition.
Q34. Can dementia patients learn new things?
A: Early-stage patients can, but difficulty increases over time.
Q35. Can physical exercise delay dementia?
A: Yes, exercise benefits brain function.
Q36. Can head injuries cause dementia?
A: Yes, traumatic injuries increase risk.
Q37. Can dementia patients feel lonely?
A: Yes, social withdrawal is common.
Q38. Can smoking increase dementia risk?
A: Yes, it damages blood vessels and brain health.
Q39. Does dementia get worse at night?
A: Many experience “sundowning.”
Q40. Can dementia cause appetite loss?
A: Yes, eating habits may change.
Q41. Can routine help manage dementia?
A: Yes, it reduces confusion.
Q42. Can dementia cause personality changes?
A: Yes, behaviour may shift dramatically.
Q43. Are hallucinations a symptom?
A: Yes, especially in Lewy body dementia.
Q44. Can dementia patients drive?
A: Only in early stages with doctor approval.
Q45. Do dementia patients need constant supervision?
A: Later stages require full-time care.
Q46. Can meditation help memory?
A: Yes, it reduces stress and improves focus.
Q47. Does loneliness increase dementia risk?
A: Yes, social isolation affects brain health.
Q48. Can dementia lead to incontinence?
A: Yes, in advanced stages.
Q49. Can hearing loss increase dementia risk?
A: Yes, untreated hearing loss affects brain function.
Q50. Should caregivers seek support?
A: Yes, caregiver counselling is very helpful.









Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!
Leave a Comment