Introduction
The keto diet has become one of India’s most popular weight-loss trends. From celebrities to influencers to fitness enthusiasts, everyone seems to be trying it. The promise is simple: rapid weight loss by reducing carbs and increasing fats. But as more people adopt the ketogenic lifestyle, experts are raising concerns about nutrition risks, long-term safety, and potential health complications.
Several studies now show that sticking to keto for months or years can result in nutrient deficiencies, hormonal changes, increased cholesterol, kidney issues, liver strain, and heart risks—especially when not supervised by a doctor or dietitian.
This comprehensive guide explains how the keto diet works, its benefits, its risks, and why long-term use may not be safe for everyone.
What Is the Keto Diet?
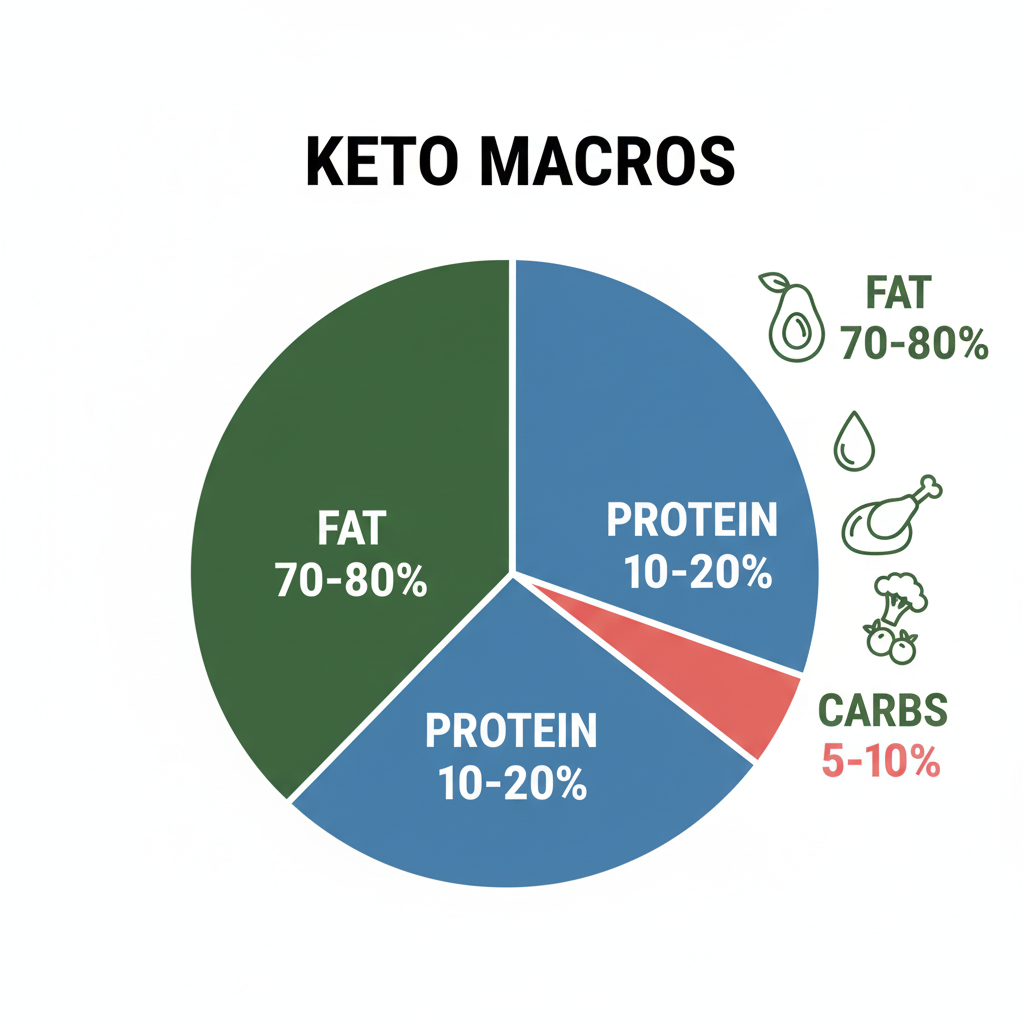
The ketogenic or keto diet is a very low-carbohydrate, high-fat eating pattern. When carbs drop to extremely low levels (20–50g/day), the body enters ketosis — a metabolic state where fat is burned for energy instead of glucose.
Typical ratios on keto:
-
70–80% fat
-
10–20% protein
-
5–10% carbohydrates
It is originally a medical diet used to treat epilepsy, not a general weight-loss plan.
How Keto Works
In normal conditions, the body uses glucose (carbs) for fuel. During ketosis:
-
Carb intake is drastically reduced.
-
The liver converts fats into ketones.
-
Ketones become the primary energy source.
-
Weight loss occurs due to fat burning and reduced appetite.
Short-Term Benefits of the Keto Diet
Keto can offer certain benefits in the short run:
1. Quick Weight Loss
Reduced carbs lead to rapid fat burning and water loss.
2. Reduced Appetite
Ketones suppress hunger hormones.
3. Improved Blood Sugar Control
Some people with insulin resistance see better sugar levels temporarily.
4. Better Focus (initially)
Ketones may improve mental clarity when the diet is followed correctly.
However, these benefits often decline or reverse with long-term keto use.
Is Long-Term Keto Diet Safe?
Experts agree: short-term keto may be safe, but long-term keto can be risky without medical supervision. New research shows multiple nutrition risks and physical complications.
Serious Long-Term Side Effects of the Keto Diet
1. Nutrient Deficiencies
Since keto restricts fruits, whole grains, legumes, and many vegetables, deficiencies can develop in:
-
Vitamin B1, B6, B9
-
Vitamin C
-
Magnesium
-
Potassium
-
Fiber
-
Antioxidants
-
Phytochemicals
This increases risks of fatigue, constipation, muscle weakness, and immunity issues.
2. High Cholesterol and Heart Risks
A high-fat diet can elevate:
-
LDL (“bad”) cholesterol
-
Triglycerides
-
Inflammation markers
Long-term, this may increase the risk of heart disease, especially in people with family history of cardiac issues.
3. Liver Damage
The liver processes fats. Consuming excessive fat continuously can cause liver strain or fatty liver, especially in:
-
Obese individuals
-
People with alcohol use
-
Those with already elevated liver enzymes
4. Kidney Stones
Long-term keto increases uric acid and calcium levels in urine, raising the risk of kidney stones. Dehydration due to low-carb diets worsens this condition.
5. Hormonal Imbalance
Especially in women:
-
Irregular periods
-
Reduced fertility
-
Thyroid dysfunction
-
Hair loss
The thyroid requires carbs to function properly, and extremely low-carb diets can interfere with hormones.
6. Gut Health Problems
Low fiber intake leads to:
-
Constipation
-
Bloating
-
Poor digestion
-
Weakened gut microbiome
Healthy carbohydrates help maintain good bacteria in the gut.
7. Mood and Mental Health Issues
Though some feel mentally clear initially, long-term keto may cause:
-
Irritability
-
Anxiety
-
Sleep disturbances
-
Low mood or depression
The brain requires some glucose for optimal functioning.
8. Bone Health Decline
Some studies show increased calcium loss and reduced bone mineral density with prolonged ketosis.
9. Muscle Loss
If not properly balanced, long-term keto can lead to loss of lean muscle mass due to inadequate protein and glycogen depletion.
Signs and Symptoms of Keto Diet Side Effects
Common symptoms include:
-
Persistent fatigue
-
Headaches
-
Irritability
-
Constipation
-
Dizziness
-
Hair fall
-
Muscle cramps
-
Bad breath
-
Heart palpitations
-
Weakness in workouts
If severe symptoms appear, immediate medical evaluation is needed.

Who Should Not Try the Keto Diet?
Keto may be unsafe for:
-
People with kidney disease
-
People with liver disease
-
Women with PCOS or thyroid issues
-
Pregnant or breastfeeding women
-
Diabetics on insulin (risk of hypoglycemia)
-
People with eating disorders
-
Athletes needing high carbs
-
People prone to nutritional deficiencies
Medical Evaluation & Diagnosis
If someone on keto experiences symptoms, doctors may test:
-
CBC
-
Liver function tests
-
Lipid profile
-
Thyroid panel
-
Vitamin levels (D, B12, iron)
-
Kidney function
-
Electrolytes
These tests help identify which deficiencies or complications are developing.
ALSO READ: How My On-air 'brain Fog' Moment Sparked A Big Debate
Treatment & Management
Doctors may recommend:
1. Balancing the Diet
Adding moderate carbs from healthier sources like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
2. Supplementation
Only based on medical testing (e.g., B12, D3, iron, magnesium).
3. Hydration and Electrolytes
Improving water intake and mineral balance.
4. Gradual Exit From Keto
Switching slowly to a more balanced diet to avoid rebound weight gain.
5. Treating Complications
Managing cholesterol, kidney issues, or hormonal imbalances if detected.
Healthier Alternatives to Keto
-
Mediterranean diet
-
Balanced low-calorie diet
-
High-fiber plant-based diet
-
Diabetes-friendly diet (doctor-guided)
-
Calorie deficit with macro balance
-
Exercise + nutrition combo
These offer safer, long-term weight-loss results.
Prevention: How to Avoid Keto Risks
-
Do not follow keto for more than 6–12 weeks without medical advice
-
Ensure regular blood tests
-
Include low-carb vegetables, nuts, seeds
-
Do not consume excessive saturated fats
-
Avoid self-designed keto plans
-
Consult a nutritionist before starting

When to See a Doctor
Seek medical help if you experience:
-
Persistent fatigue
-
Severe constipation
-
Chest discomfort
-
Palpitations
-
Very high cholesterol
-
Irregular periods
-
Kidney pain
-
Hair loss
-
Anxiety or depression
Conclusion
The keto diet can help with short-term weight loss, but long-term use carries significant nutrition risks and may harm the heart, liver, kidneys, hormones, and gut. Like any restrictive diet, it must be approached with balance and medical guidance. Sustainable weight loss comes from consistent dietary habits—not extreme restrictions.
If you're considering keto or facing side effects, seek professional advice to protect your long-term health.
50 FAQs
-
Is keto diet safe long term?
Long-term keto is linked to nutrient deficiencies, heart risks, and organ strain. -
What is ketosis?
A metabolic state where the body burns fat instead of carbs for energy. -
How fast does weight loss happen on keto?
Many lose weight in the first 2–4 weeks due to fat and water loss. -
Can keto damage the liver?
Yes, long-term high-fat intake may strain the liver. -
Does keto cause high cholesterol?
It can raise LDL cholesterol in some people. -
Can keto cause kidney stones?
Yes, due to increased uric acid and dehydration. -
Is keto good for diabetics?
Only under strict medical supervision. -
Can keto affect periods?
Yes, it may cause irregular menstrual cycles. -
Is keto safe for teenagers?
No, it can cause deficiencies during growth years. -
Does keto cause hair fall?
Yes, due to nutrient deficits. -
Is keto effective for PCOS?
Short-term yes, long-term may harm hormones. -
Can keto harm the heart?
High-fat intake may raise cardiac risks. -
Can I eat fruits on keto?
Only limited low-carb fruits like berries. -
Is constipation common on keto?
Yes, due to low fiber intake. -
How much weight can I lose?
Ranges 2–10 kg initially depending on body type. -
Can keto cause anxiety?
In some people, prolonged keto affects mood. -
Is keto safe in pregnancy?
No, it is unsafe. -
Can keto cause bad breath?
Yes, due to ketones. -
Can I exercise on keto?
Yes, but intense workouts may feel harder. -
Is keto expensive?
High-fat foods can increase monthly grocery costs. -
Can keto reverse diabetes?
It can improve sugar levels short term but must be supervised. -
Does keto reduce hunger?
Yes, ketones suppress appetite. -
Is keto harmful for thyroid?
Long-term keto may slow thyroid function. -
Is keto safe for seniors?
Generally not recommended. -
What foods are allowed?
Meat, eggs, paneer, cheese, nuts, oils, low-carb vegetables. -
What foods are restricted?
Rice, wheat, fruits, potatoes, legumes, sugar. -
Can keto cause low BP?
It may lower blood pressure initially. -
Is keto suitable for vegetarians?
Possible but challenging. -
Does keto improve focus?
Sometimes initially; long-term results vary. -
Is keto harmful for liver patients?
Yes, avoid keto. -
Can keto cause dehydration?
Yes, due to loss of electrolytes. -
Can I drink alcohol on keto?
Limited and low-carb options only. -
Can keto cause weakness?
Yes, if carb restriction is too extreme. -
Should I take supplements?
Only after doctor recommendation. -
Is keto sustainable?
Most people find it difficult long term. -
Can keto cause low blood sugar?
Yes, particularly in diabetics on medication. -
Does keto affect sleep?
It may disturb sleep initially. -
Can keto cause leg cramps?
Yes, due to magnesium loss. -
Does keto affect digestion?
Low fiber may cause gut imbalance. -
Can keto cause mood swings?
Yes, due to hormonal shifts. -
Does keto increase uric acid?
Yes, increasing gout risk. -
Can keto cause nausea?
Yes, especially early on. -
Is keto good for muscle gain?
Not ideal; carbs are needed for growth. -
Can keto cause headaches?
Common during early adaptation. -
Why does keto cause fatigue?
Low carbs reduce glycogen stores. -
Is keto good for fatty liver?
Short-term may help; long-term may worsen. -
Can keto affect immunity?
Nutrient deficits may lower immunity. -
Can keto cause dizziness?
Yes, due to electrolyte loss. -
Should I consult a doctor before starting?
Yes, especially if you have health conditions. -
Is keto the best diet for weight loss?
Not for everyone; balanced diets work better long term.
Quickobook CTAs
-
Book an appointment with a nutritionist on Quickobook for safe weight-loss planning.
-
Consult a general physician for keto side effects like fatigue, cholesterol, or hormonal symptoms.
-
Use Quickobook online consultations for dietary guidance from home.
Disclaimer
This blog is for educational purposes only. It does not replace medical advice. Always consult a qualified doctor or nutritionist before starting or stopping any diet.









Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!
Leave a Comment