Introduction
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are common, but many people do not realize that the earliest signs can be very mild—or completely silent. Both men and women may develop symptoms days, weeks, or even months after exposure. Because these signs are subtle, many people continue their daily life without knowing they are infected. This increases the risk of complications and unknowingly spreading the infection to partners.
Understanding the early symptoms of STIs is essential for protecting your health, preventing long-term damage, and practicing safe sex. Whether you are sexually active, planning to be, or simply want to stay informed, knowing these warning signs can help you take action at the right time.
This detailed guide covers the earliest STI symptoms in men and women, the types of infections, how they spread, when to seek medical help, and how to stay protected through safe sex practices.
Understanding STIs and How They Spread
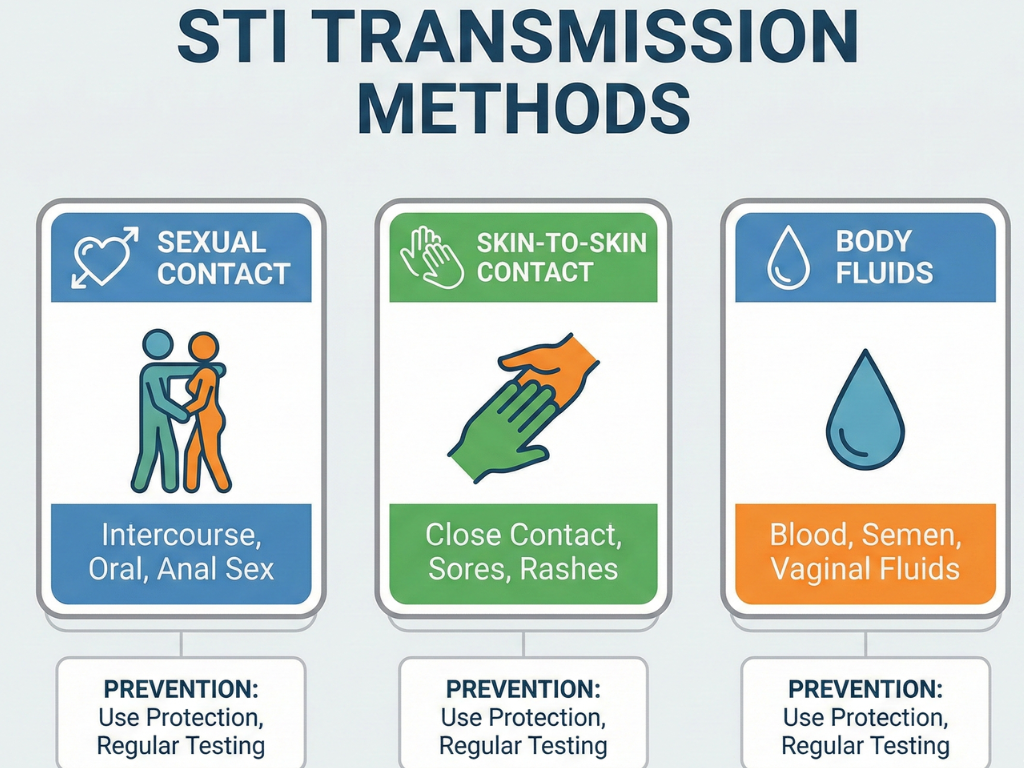
What STIs actually are
STIs (sexually transmitted infections) are infections passed from one person to another through sexual contact—vaginal, oral, or anal sex. Some spread through skin-to-skin contact. Anyone who is sexually active can get an STI, even if it is their first time.
Common STIs in India
-
Chlamydia
-
Gonorrhea
-
Syphilis
-
Herpes
-
HPV (Human Papillomavirus)
-
Trichomoniasis
-
Hepatitis B
How STIs spread
-
Unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex
-
Skin-to-skin contact in genital areas
-
Contact with infected body fluids
-
Sharing needles
-
From mother to baby during childbirth
Understanding how STIs spread helps in prevention and early diagnosis.
Why STI Symptoms Are Often Missed
Symptoms may be mild
Many STIs start with very light symptoms that look like normal irritation, dehydration, stress, or allergies.
Some infections show no symptoms
STIs like chlamydia, HPV, and HIV can stay hidden for months or years.
Embarrassment or fear
Some people avoid checking symptoms due to shame or fear of judgment.
Confusion with hygiene issues
A discharge or rash may be mistaken for sweating, soap reaction, or tight clothing.
Missing early symptoms allows the infection to grow and spread.
Early STI Symptoms in Men
Unusual penile discharge
A thick, watery, yellowish, or greenish discharge is a major sign of chlamydia or gonorrhea.
Burning or pain during urination
Pain while peeing is one of the earliest STI symptoms in men and should never be ignored.
Pain or swelling in testicles
Some infections cause discomfort or swelling in one or both testicles.
Rashes or bumps on the penis
Small bumps, red spots, or painful blisters can indicate herpes or HPV.
Itching around the genitals
Persistent itching that doesn’t improve with basic hygiene can be caused by an STI.
Blood in urine or semen
Rare but serious symptom, often linked to infection or inflammation.
Pain during ejaculation
Discomfort while ejaculating may signal infection in the urethra or prostate.
Flu-like symptoms
Fatigue, fever, and muscle pain can appear during early HIV infection.
ALSO READ: Is Screen-time Burnout Draining You? Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Early STI Symptoms in Women
Unusual vaginal discharge
Change in color, smell, or texture may indicate chlamydia, gonorrhea, or trichomoniasis.
Burning sensation while urinating
Pain while peeing is a major early sign among women.
Bleeding between periods
Spotting or bleeding not linked to menstruation may be an STI warning.
Pain during sex
Painful intercourse can indicate pelvic infections.
Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
This is often seen in infections like PID (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease).
Rashes or sores around the vagina
Blisters or bumps are common signs of herpes or HPV.
Vaginal odor
A strong fishy smell often points to infection.
Itching or redness
Persistent irritation around the vagina may point to an STI or other infection.
Fever or body aches
Systemic symptoms may occur in untreated infections.
Common STI Symptoms Shared by Both Men and Women
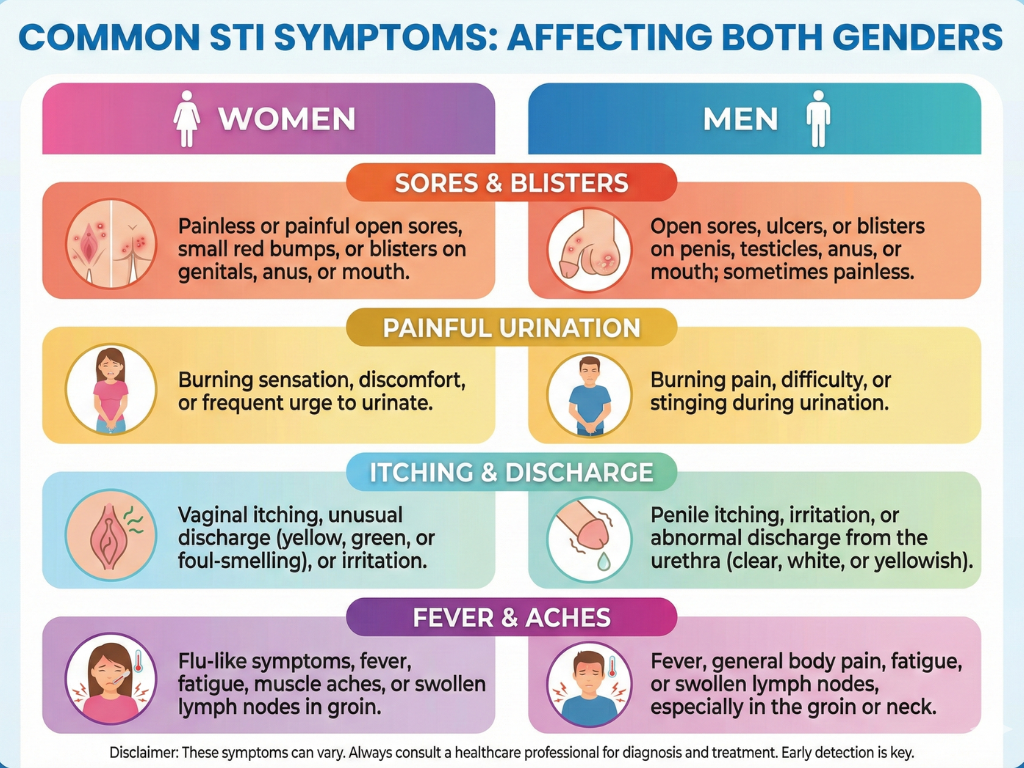
Pain during sex
Inflammation or infection can make intercourse uncomfortable.
Sores, ulcers, or blisters
Painful or painless sores may appear in herpes or syphilis.
Swollen lymph nodes
Lymph nodes in the groin may swell due to infection.
Fever and fatigue
Common during early viral infections like HIV or herpes.
Anal itching or discharge
Occurs in infections spread through anal sex.
General irritation in the genital area
Tight clothes or sweating can worsen symptoms, but the infection is the underlying cause.
Early Symptoms of Specific STIs
Chlamydia
-
Mild discharge
-
Burning during urination
-
Lower abdominal pain
-
Often symptomless
Gonorrhea
-
Thick yellow or green discharge
-
Painful urination
-
Pelvic pain
Syphilis
-
Rash on palms or feet
-
Fever and swollen nodes
Herpes (HSV)
-
Tingling sensation
-
Painful blisters or sores
-
Burning and itching
HPV
-
Genital warts
-
Itching
-
Often silent
HIV
-
Flu-like symptoms
-
Night sweats
-
Fatigue
-
Swollen lymph nodes
Trichomoniasis
-
Strong-smelling discharge
-
Itching
-
Pain during urination
Risks of Ignoring STI Symptoms
Untreated STIs can lead to:
For women
-
Infertility
-
PID (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease)
-
Ectopic pregnancy
-
Chronic pelvic pain
For men
-
Prostate infections
-
Testicular damage
For both
-
Chronic pain
-
Higher HIV risk
-
Spread to partners
-
Long-term organ damage
Early diagnosis prevents these complications.
Diagnosis and Testing
Doctors may suggest the following:
Urine tests
Detect bacterial infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea.
Swab tests
Check discharge or vaginal/penile fluid.
Blood tests
Detect syphilis, HIV, and hepatitis.
Pap smear / HPV test
Checks for HPV in women.
Physical examination
For sores, bumps, and pain.
Testing is private, confidential, simple, and widely available across India.
Treatment Options
Antibiotics
Effective for bacterial infections like chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis.
Antiviral medicines
Manage herpes and HIV.
Pain relievers
For associated discomfort.
Partner treatment
Both partners must be treated to avoid reinfection.
Counselling
Helps deal with emotional stress.
Doctors decide the dosage—never self-medicate.
Prevention: Practicing Safe Sex
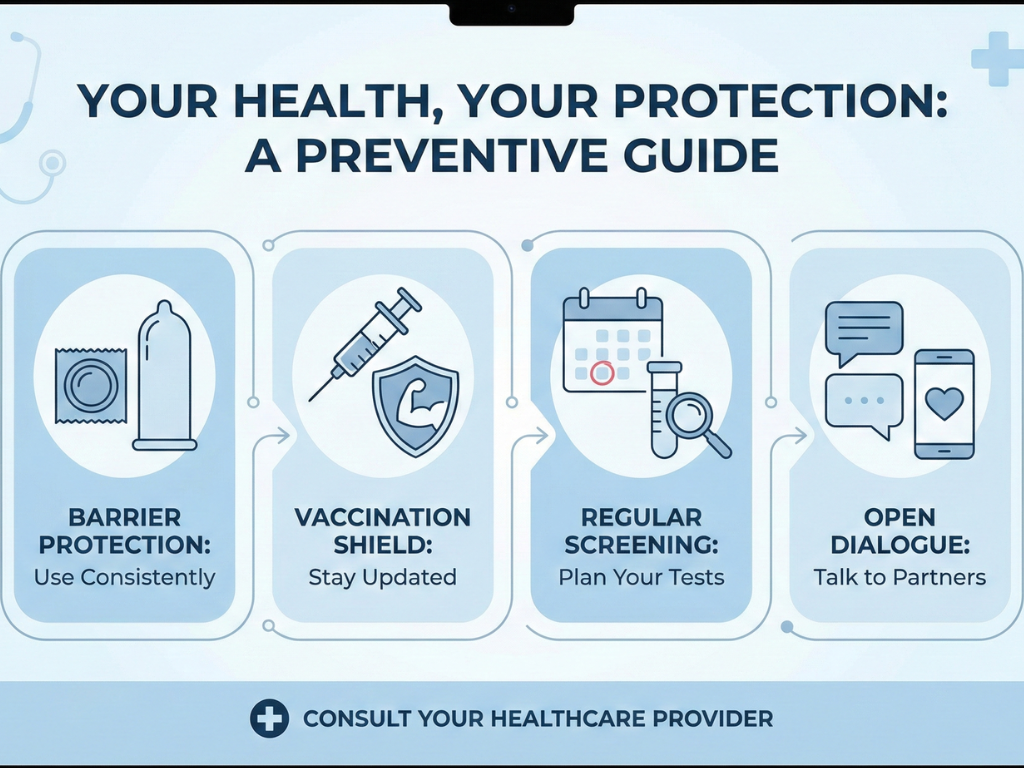
Use condoms correctly
Condoms reduce the risk of most STIs.
Get tested regularly
Especially if you have new or multiple partners.
Limit risky behavior
Avoid sex under alcohol or drug influence.
Discuss sexual history openly
Honest conversations help reduce risk.
Avoid sharing towels or intimate items
Some infections spread indirectly.
Vaccination
HPV and Hepatitis B vaccines offer strong protection.
Avoid unprotected sex
Even once can cause infection.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical help if you notice:
-
Unusual discharge
-
Burning while urinating
-
Pain during sex
-
Pelvic or testicular pain
-
Sores or bumps
-
Fever with genital symptoms
-
Strong odor
-
Bleeding between periods
Do not wait for symptoms to worsen.
Conclusion
STI symptoms in men and women can start mild but become dangerous if ignored. Early detection and treatment are the keys to preventing long-term complications. Practicing safe sex, using condoms, and getting regular check-ups can protect you and your partner.
Your sexual health matters. Awareness and action make all the difference.
Quickobook CTA
If you notice STI symptoms or want confidential sexual health advice, book an appointment with expert gynecologists, urologists, or general physicians on Quickobook.
Fast booking • Private consultations • Trusted doctors
FAQs
Q1. What are early STI symptoms in men?
A. Discharge, burning while urinating, rashes, and itching.
Q2. What are early STI symptoms in women?
A. Unusual discharge, spotting, pelvic pain, and itching.
Q3. Can STIs show no symptoms?
A. Yes, many STIs are silent.
Q4. Do condoms fully prevent STIs?
A. They greatly reduce risk but are not 100% protective.
Q5. Can oral sex spread STIs?
A. Yes, infections like herpes and gonorrhea can spread orally.
Q6. Is itching a sign of STI?
A. Yes, especially if persistent.
Q7. What does smelly discharge mean?
A. It can be a sign of infection.
Q8. Does an STI cause fever?
A. Yes, some infections cause fever and fatigue.
Q9. How soon do STI symptoms appear?
A. Between 2 days and several months.
Q10. Does STI cause stomach pain?
A. Yes, especially in women.
Q11. Can men get pelvic pain?
A. They may develop testicular or lower abdominal pain.
Q12. Are bumps on genitals serious?
A. They may indicate herpes or HPV.
Q13. Can STIs cause infertility?
A. Yes, untreated infections can.
Q14. Does painful urination always mean STI?
A. Not always, but it should be checked.
Q15. Can syphilis be painless?
A. Yes, the first sore is often painless.
Q16. What causes blood in discharge?
A. Severe infection or irritation.
Q17. How do doctors test for STIs?
A. Urine, blood, or swab tests.
Q18. Is HIV an STI?
A. Yes, it spreads through sexual contact.
Q19. Can kissing spread STIs?
A. Rarely, except for oral herpes.
Q20. Is condom use enough for safe sex?
A. It reduces but does not eliminate risk.
Q21. Can untreated STIs cause pain during sex?
A. Yes, due to inflammation.
Q22. Can STIs affect pregnancy?
A. Yes, they can cause complications.
Q23. Are women more vulnerable?
A. Yes, female anatomy increases risk.
Q24. Can STIs spread through touch?
A. Some can, through skin contact.
Q25. Can you get STI from toilet seats?
A. No, this is a myth.
Q26. Is discharge normal?
A. A sudden change suggests infection.
Q27. Can stress cause STI-like symptoms?
A. Stress does not cause STIs.
Q28. Can antibiotics cure all STIs?
A. Only bacterial ones.
Q29. Are viral STIs permanent?
A. Some like herpes stay lifelong.
Q30. Can condoms break?
A. Yes, incorrect use may cause breakage.
Q31. What is the safest STI prevention?
A. Correct condom use + testing.
Q32. Do STIs always cause pain?
A. No, some are painless.
Q33. Can STIs cause vaginal odor?
A. Yes, strong odor indicates infection.
Q34. Can STIs cause lumps?
A. Yes, especially HPV.
Q35. Can men have no symptoms?
A. Yes, many show later signs.
Q36. How often should I get tested?
A. Every 6–12 months or after a new partner.
Q37. Can multiple partners increase STI risk?
A. Yes, significantly.
Q38. Does alcohol increase STI risk?
A. Yes, due to reduced judgment.
Q39. Can STIs spread through oral contact?
A. Yes, several can.
Q40. Are condoms required for oral sex?
A. Yes, to reduce infection risk.
Q41. Can you get STI from kissing neck/genitals?
A. Some infections can spread through contact.
Q42. Are genital sores serious?
A. Yes, always check them.
Q43. Can STI symptoms go away on their own?
A. Symptoms may go, infection stays.
Q44. Can I check STI signs at home?
A. You can notice symptoms, but testing is needed.
Q45. Can STIs cause mood changes?
A. Severe infections can affect mood and energy.
Q46. Can STIs cause night sweats?
A. Yes, especially during early HIV infection.
Q47. Can you get STI from sharing towels?
A. Rare but possible.
Q48. Can STIs cause urinary problems?
A. Yes, many cause burning or pain.
Q49. When should I see a doctor?
A. As soon as symptoms appear.
Q50. Can Quickobook help me book sexual health doctors?
A. Yes, Quickobook lets you book private appointments quickly.








Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!
Leave a Comment